

CA SiteMinder® can protect resources using Windows credential collectors (NTCs). Users submit their credentials to the NTC, then the NTC logs the user in to the IIS web server. The IIS web server authenticates the user. The NTC redirects the user to the protected (TARGET) resource after authentication.
The NTC normally encodes the characters in the TARGET portion of the URL during the request, but not during the redirect after authentication. You can change your agent configuration so that the TARGET portion of the URL is encoded during the redirect. The following illustration describes this behavior:
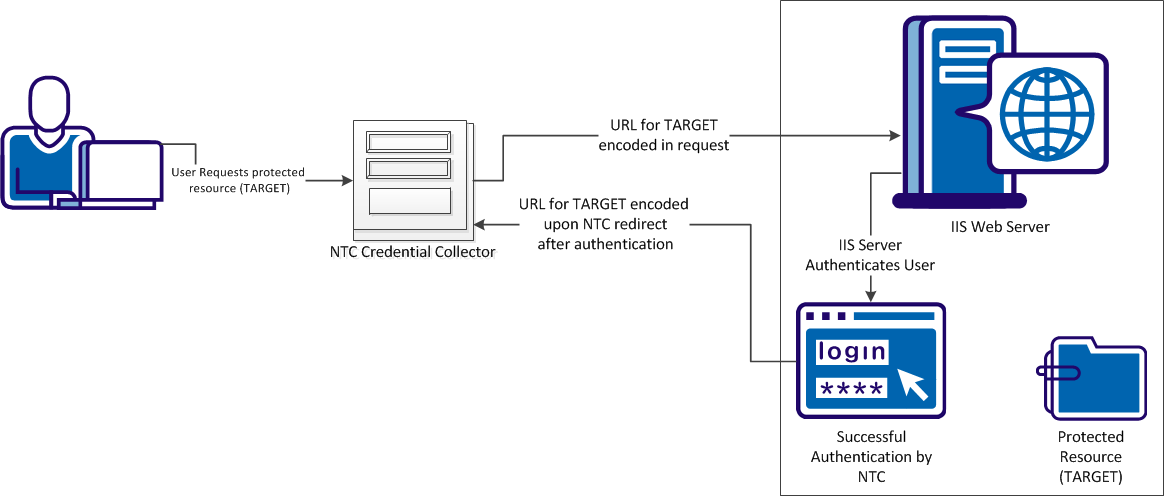
The following illustration shows the process of allowing the NTC to encode URLs during requests for protected resources:
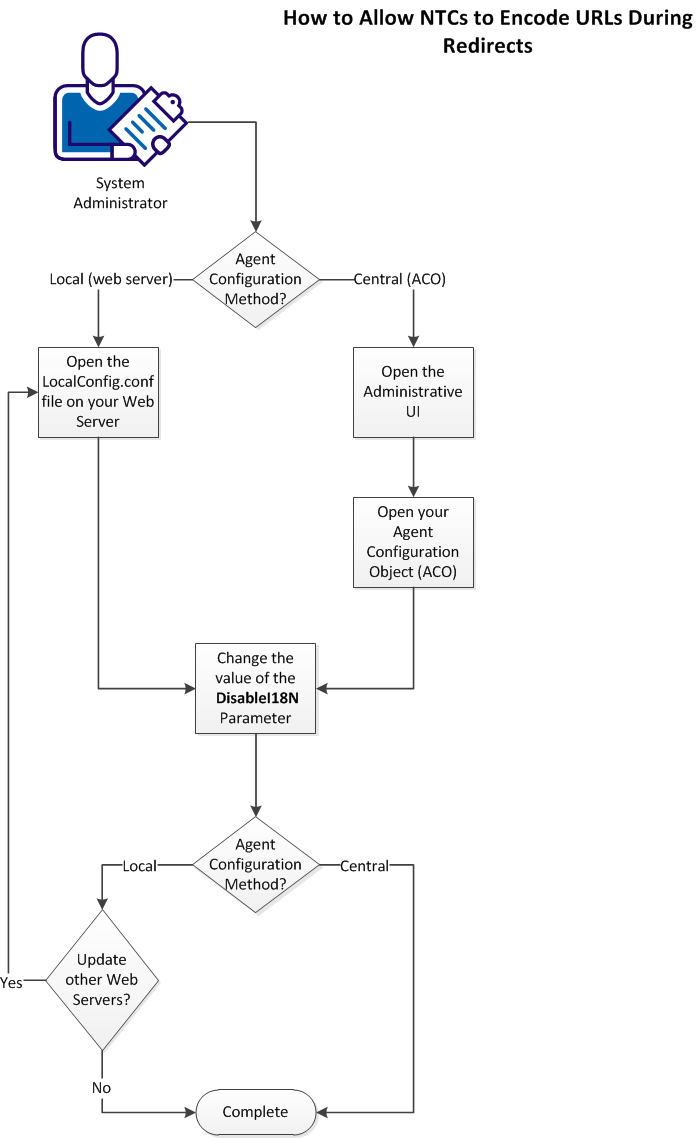
To allow the NTC to encode URLs during re–directs to protected resources, follow these steps:
The NTC uses encoded URLs during redirects to protected resources.
Open the Administrative UI to Change Policy Server Objects
Change the objects on your Policy Server by opening the Administrative UI.
Follow these steps:
https://host_name:8443/iam/siteminder/adminui
Specifies the fully qualified Administrative UI host system name.
Note: If your superuser account password contains dollar‑sign ($) characters, replace each instance of the dollar-sign character with $DOLLAR$. For example, if the CA SiteMinder® superuser account password is $password, enter $DOLLAR$password in the Password field.
Change the Value of the DisableI18N parameter in your Agent Configuration Object
You can configure Windows credential collectors to process HTTP encoded characters in target URLs for centrally configured web agents. Centrally–configured web agents use parameter settings stored in an Agent Configuration object on the Policy Server.
Follow these steps:
A list of Agent Configuration objects appears.
Click the edit icon in the line Agent Configuration Object you want.
The Modify Agent Configuration dialog appears.
Specifies how the Windows credential collector (NTC) processes the TARGET URL during authentication when the characters of the TARGET URL use HTTP encoding. When the value of this parameter is no, any characters in the URL are decoded during authentication. The decoded characters are used in the redirect to the TARGET resource. When the value of this parameter is yes, characters in the TARGET URL are not decoded during authentication. Any characters using HTTP encoding remain encoded before and after authentication.
Default: No.
The Edit Parameter dialog appears.
The Edit Parameter dialog closes, and the Modify Agent Configuration dialog appears.
Specifies the character sequences that cannot be used in URL requests. The Web Agent checks the characters in the URL that occur before the "?" character against the list in this parameter. If any of the specified characters are found, the Web Agent rejects the request.
You can specify the following characters:
Separate multiple characters with commas. Do not use spaces.
You can use the bad URL characters in CGI parameters if the question mark (?) precedes the bad URL characters.
Default: Disabled (all characters are allowed).
Limits:
The Edit Parameter dialog appears.
,%25
The Edit Parameter dialog closes, and the Modify Agent Configuration dialog appears.
The Modify Agent Configuration dialog closes, and a confirmation message appears.
Your changes will be applied the next time the Web Agent polls the Policy Server.
Change the Value of the DisableI18N parameter in your LocalConfig.conf File
You can configure Windows credential collectors to process HTTP encoded characters in target URLs. Locally–configured web agents use parameter settings stored in a configuration file on each web server.
Follow these steps:
Locate the LocalConfig.conf file on your web server. Use the examples in the following list to locate the file on your type of web server:
web_agent_home\bin\IIS
Oracle_iPlanet_home/https-hostname/config
Apache_home/conf
Specifies how the Windows credential collector (NTC) processes the TARGET URL during authentication when the characters of the TARGET URL use HTTP encoding. When the value of this parameter is no, any characters in the URL are decoded during authentication. The decoded characters are used in the redirect to the TARGET resource. When the value of this parameter is yes, characters in the TARGET URL are not decoded during authentication. Any characters using HTTP encoding remain encoded before and after authentication.
Default: No.
Specifies the character sequences that cannot be used in URL requests. The Web Agent checks the characters in the URL that occur before the "?" character against the list in this parameter. If any of the specified characters are found, the Web Agent rejects the request.
You can specify the following characters:
Separate multiple characters with commas. Do not use spaces.
You can use the bad URL characters in CGI parameters if the question mark (?) precedes the bad URL characters.
Default: Disabled (all characters are allowed).
Limits:
Specify any quotation marks (") with the URL-encoded equivalent of %22. Do not use ASCII.
,%25
Windows credential collectors are allowed to process HTTP encoded characters in TARGET URLs.
You can configure any of the following settings to help improve the performance of your credential collectors:
During forms authentication, the Web Agent makes an IsProtected call to the Policy Server to determine if the requested resource is protected. After this first call, the Web Agent typically makes an additional IsProtected call to the Policy Server. This second call establishes a realm context so that the Web Agent can log a user in with an FCC to access a protected resource. You can control whether the Web Agent makes this additional call using the following parameter:
Specifies whether the Web Agent makes an additional IsProtected call to the Policy Server to establish a realm context so that the Web Agent can log a user in to access a protected resource.
When this parameter is set to no, the Web Agent uses the realm information obtained from its initial IsProtected call to the Policy Server instead.
Default: Yes
To improve performance by disabling the FCC realm context confirmation, set the value of the FCCForceIsProtected parameter to no.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|