

The modeled Finance service provides the necessary information to quickly detect and resolve issues that cause service degradation. Consider this simple service condition, displayed from the Topology view of the Operations Console as shown in the following graphic:
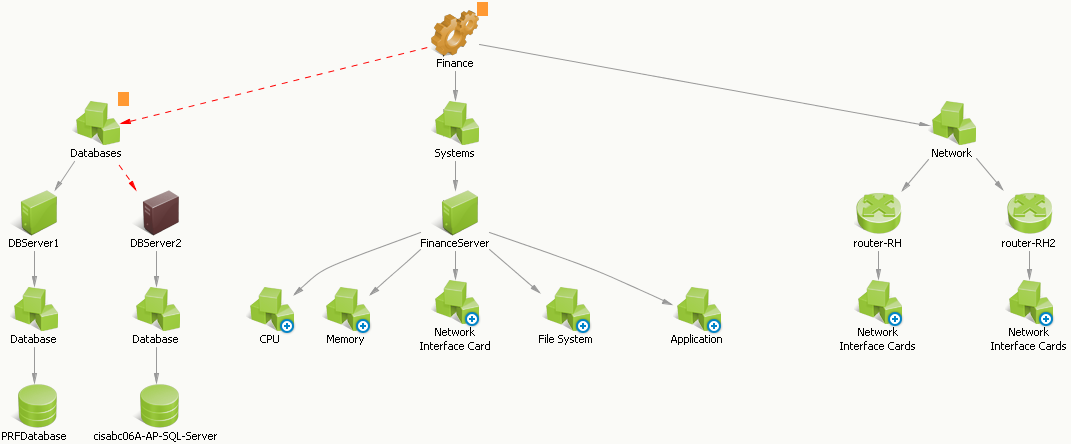
The conditions appear and are resolved as follows:
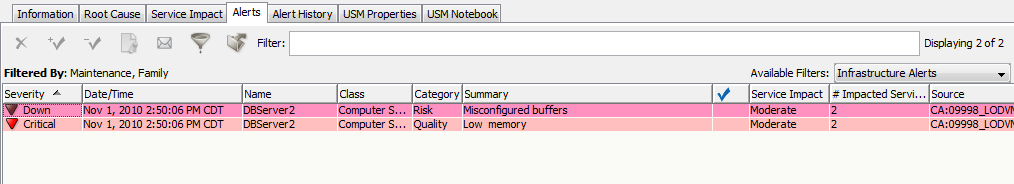
These infrastructure alerts originated from the source domain manager (in this case, CA Insight DPM) and indicate Down and Critical alerts on the DBServer2 CI. If configured, escalation policies could perform specified actions on the alert, such as opening a help desk ticket or sending an email to a technician.
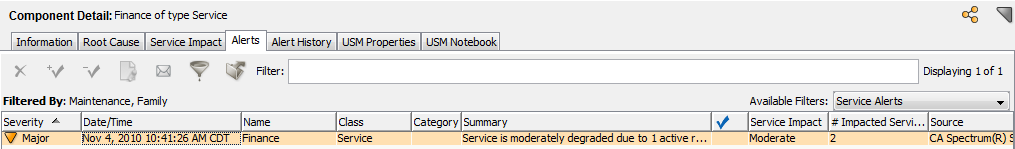
The Major severity results from the service impact value of 20 as shown in the following graphic:
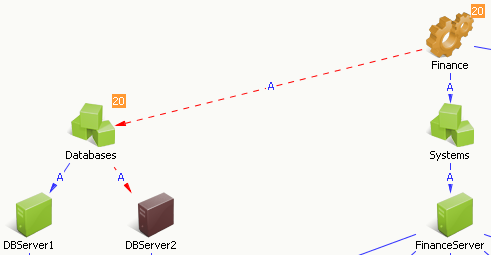
CA SOI calculates the impact based on the severity of the root cause alert and the significance of the alerted CI. In this case, the root cause alert is the Down alert because it is a higher severity than the Critical alert, which is confirmed in the Root Cause tab. If other areas of the service had a similar severity with a higher CI significance (FinanceApp, for example), the service impact would be greater, and this condition would instead aggregate to the service level as the root cause condition.

Notice that service quality and risk are both affected, because the Down alert belongs to the Risk category, and the Critical alert belongs to the Quality category. Health is a reflection of the worst state held by quality or risk.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|