Your product provides focal point management to support multisystem operation (that is, management at a focal point with subordinates and agents feeding information to it) as follows:
Supports full connectivity between multiple regions. Regions linked in this way are known as focal point regions. (A standalone region is also regarded as a focal point region.)
When regions are communicating with each other, authorized users can monitor and control all managed resources from any terminal connected to any region.
Enables you to reduce the amount of traffic in your multisystem environment. You link subordinates to focal point regions that provide central monitoring and control. A subordinate has visibility and control of the locally managed file transfers and supporting resources only.
Enables you to manage file transfers and supporting resources on a remote system without having to establish a region on that system.
In a multisystem environment, each region can run independently of the other regions. If no communication links are available, each region still provides full monitoring, control, and automation of its own managed resources.
To link a focal point region to another focal point region, or to link a subordinate to a focal point region, you need to link and synchronize the regions.
The link established between two regions in a multisystem environment is an INMC link. The link is used to pass knowledge base updates, status change notification, and other information between the two regions. The link can use any combination of the following communications protocols: VTAM, TCP/IP, and EPS. VTAM is the default.
For each region, the MULTISYS parameter group specifies the available communication access methods. If TCP/IP is used, ensure that the SOCKETS parameter group is activated.
The INMC link between any two regions uses the access methods enabled by both regions (that is, the intersection of the two MULTISYS parameter groups). When multiple access methods are enabled, the link can use all these methods. This improves reliability because the link functions when one of the enabled methods is available.
When you plan your multisystem environment, ensure the following:
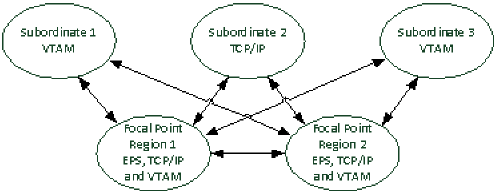
Example: Focal Point Regions Support All Access Methods
This example shows a multisystem link configuration when the focal point regions support ESP, TCP/IP, and VTAM. The subordinate regions can support any one of these access methods.
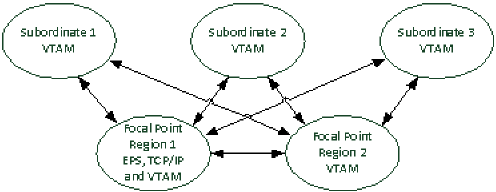
Example: One Focal Point Region Supports VTAM Only
This example shows a multisystem link configuration when a focal point region supports VTAM only. The subordinate regions must support VTAM.
With the EPS access method, you can use the Sysplex cross-system coupling facility (XCF) to implement your multisystem environment.
Note: To support the EPS access method, a SOLVE SSI region must be active in each of the cooperating systems and must be registered to XCF.
To register the SOLVE SSI region to XCF, add the XCF=YES parameter to the SOLVE SSI.
All participating CA NetMaster FTM and SOLVE SSI regions must also include the Sysplex feature (INC=(SYSPLEX)) in their RUNSYSIN and started task members, respectively.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. |
|