The multistep authentication model is like the CA SiteMinder cookie-based single sign-on implementation, in which WS‑Security headers or SAML Session Ticket assertions take the place of the cookie.
In the multistep authentication model, a single web service is responsible for authenticating all incoming web service requests. This authentication service verifies a web service consumer’s identity and returns an XML message with authentication data in the form of WS‑Security headers or a SAML Session Ticket assertion. The web service consumer can then use this to add to subsequent requests to facilitate authentication by other associated web services.
The process that the web service consumer goes through when making a request has two phases:
The following illustration shows how request are processed in the multistep authentication service model:
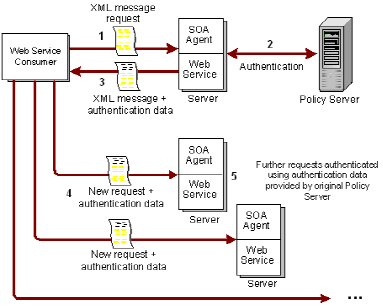
After authentication, the request goes through the authorization process. A response attribute associated with the authorizing policy causes the Policy Server to generate a response which it sends to the SOA Agent, instructing it to return authentication data to the web service.
Appropriate authentication schemes for initial authentication by the authentication web service in the multistep authentication model are as follows:
The authorizing policy for the authentication web service should trigger one of the following response types:
These responses instruct the SOA Agent to pass authentication data in the form of WS‑Security headers or SAML Session Ticket assertions (as appropriate) back to the web service consumer for use in requests to associated web services. The associated web services should be protected using the corresponding authentication scheme:
Note: SOA Agents can be configured to accept information from a CA SiteMinder session (SMSESSION) cookie in the HTTP header of a request as a means of authenticating a client and always add such cookies to request headers upon successful authentication and authorization. CA SiteMinder session cookies can therefore be used to implement multistep authentication within an all CA SiteMinder/SOA Security Manager environment.
| Copyright © 2011 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA Technologies about this topic |