

Links between operators define dependencies. The links act on the results that each operator produces. Links define the order and logic of a process as it flows.
Different kinds of actions have different predefined results or outcomes:
The application calculates these outcomes to determine the next exit conditions, ports, and links to activate, in a logical sequence. For example, you can add a custom port on some operators and can define the port to activate when an expression returns a True value.
Exit conditions on an operator are not mutually exclusive. If the product evaluates more than one exit condition as True, all of exit conditions are processed. Processing multiple exit conditions on a single operator can start subsequent simultaneous processing of multiple branches.
When a process runs, the product activates its operators only once. When a link leads to a previously activated operator, the product does not reprocess the destination operator and the branch that the link extends ends.
Note: Links are joined to operators at small connection points called ports.
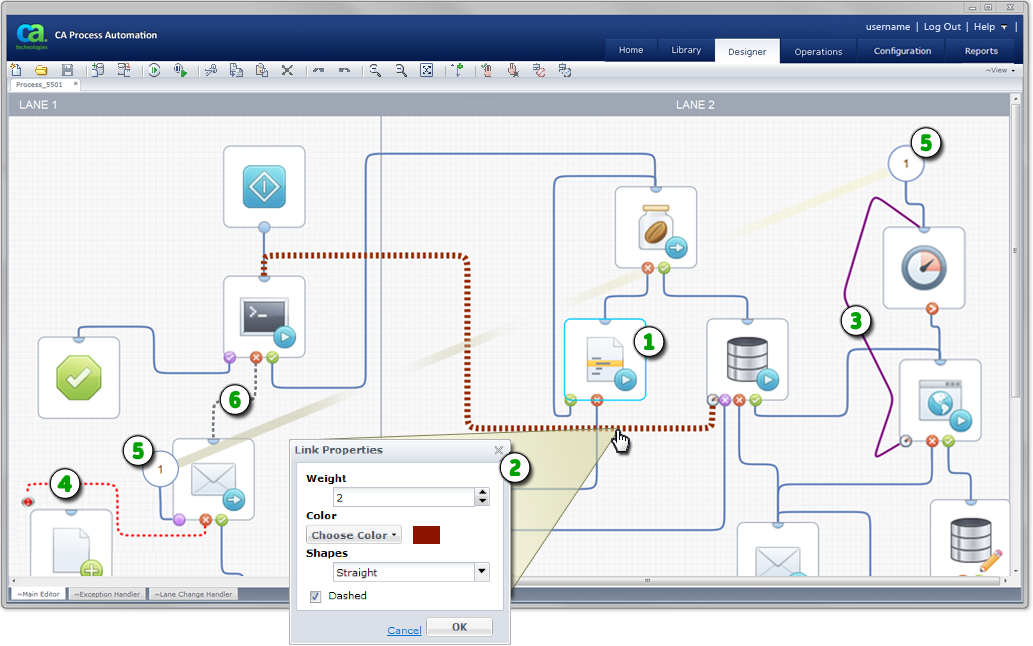
|
Item: |
Description: |
|---|---|
|
|
Selected Operator: Click an operator to view its dataset variables, pages, and properties. Right-click an operator to add an exit port. |
|
|
Link Properties: Do one of the following to adjust the appearance of a link:
Select the thickness, color, shape, and dashed appearance of each link. |
|
|
Link Line Shape: Instead of ordinary orthogonal lines, this purple link appears with straight line segments. You can stretch and position all links as necessary. |
|
|
Stopped Link: This link has been forced to stop. As an example, consider a process that is looping, waiting for some event, processing that event, and looping repeatedly. When a parallel process branch determines that the original looping process must stop, it can use the stopped port and link to stop the loop. |
|
|
Broken Link: Break a link to split a long circuitous route into two numbered stubs. The split links are easier to view and manage. To rejoin the numbered stubs, right-click the circled link number, then select Join Links. |
|
|
Disabled Link: This dashed gray link to indicates that it is temporarily disabled. Right-click the link to re-enable it. |
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|