

Specifies the distinguished name of the object under which you want to create the new LDAP object.
Specifies the name of the new LDAP object.
Be sure to add the LDAP attribute to the name of the new LDAP object. The attribute could be "ou", "cn", "uid", and so on, and depends on the type of LDAP object being created.
If checked, the "objectclass" Attribute Values Array will be used for this request.
Specifies the array containing the values of the "objectclass" Attribute. This dataset field must be defined as an array (indexed string). If Use the specified array field for Object's "objectclass" Attributes Values is checked, this field will be used.
Specifies the values of the "objectclass" Attribute. If the Use the specified array field for Object's "objectclass" Attributes Values is unchecked, this field will be used.
The "objectclass" is the LDAP attribute that defines the type of the new object.
This is an array of value maps containing additional LDAP attributes to be set for the new object. Each value map's Key must be of type string, Value must be of type string or array of strings (indexed string). The key must be named Keys and the value must be named Values.
The user can set the Values field to be of type string to create single-valued LDAP attributes for the new LDAP object being created. For example:
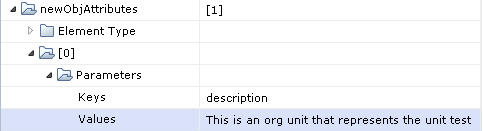
The object newObjAttributes is an indexed ValueMap whose key fields are called Keys and are of type string and value fields are called Values and are of type string.
Alternatively, the user can set the Values field to be of type array of strings (indexed string) to create multi-valued LDAP attributes for the new LDAP object being created.
The object newObjAttributes2 is an indexed ValueMap whose key fields are called Keys and are of type string and value fields are called Values and are of type indexed string. In this case the user can create both single-valued and multi-valued LDAP attributes for the new LDAP object being created.
For example:
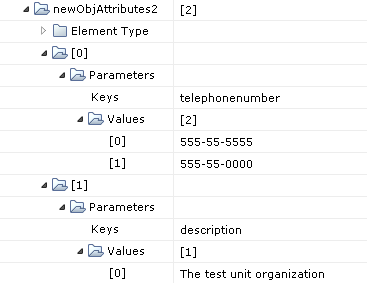
Within the same newObjAttributes2 object, we have a multi-valued telephonenumber attribute and also a single-valued description attribute.
Note that if the same key appears multiple times within the indexed ValueMap, only the last value associated with the key will remain.
Note that the attribute names entered in the Additional Object's LDAP Attributes Value Maps must be the LDAP names of these attributes as specified in the LDAP server schema. For instance, to set the value of the attribute "Last name" you must use the LDAP name of this attribute: "sn", to set the value of the attribute "First Name", you must use the attribute "givenname", and so on. See Common LDAP Attribute Names.
The LDAP names are different from the attributes display names.
Most LDAP servers differ in the display names of the LDAP attributes, but they all must support the LDAP names of these attributes, thus the reason why we require the usage of the LDAP names of the attributes instead of the display names.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|