

The following example shows a sample process record dump report:
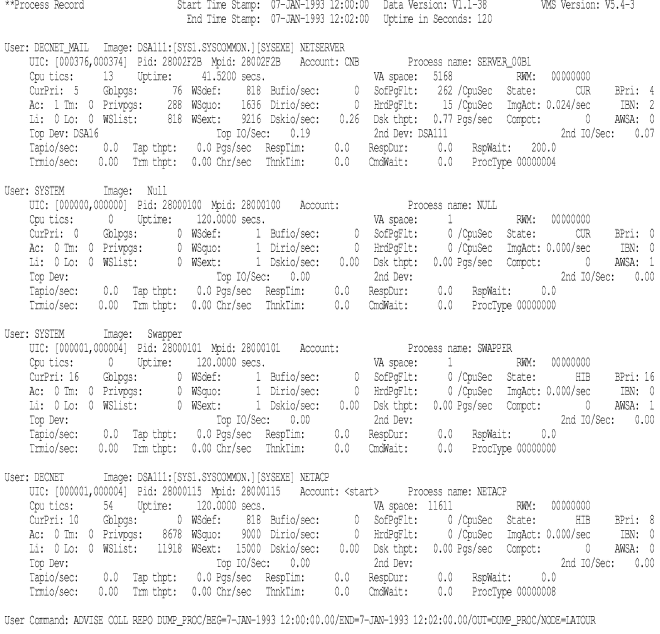
The following table describes the headings in the process record section of the dump report:
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
User |
User name associated with the PID |
|
Image directory |
Location from which image came |
|
Image |
Name of the image the user is executing |
|
UIC |
The UIC of the process |
|
Pid |
Process ID number |
|
Mpid |
The master process ID number or owner process ID number |
|
Account |
The account name |
|
Process name |
The process name |
|
Cpu tics |
CPU time charged to the image in 10-millisecond units. This metric equals the same number with its decimal point moved two places to the right. For example, 100 tics equals 1.00 second. |
|
Uptime |
Up time per image in seconds. |
|
VA space |
Peak virtual address space used |
|
RWM |
Resource wait mask |
|
CurPri |
Current priority |
|
Gblpgs |
Average count of global pages |
|
WSdef |
Default working set size |
|
Bufio/sec |
Buffered I/O rate |
|
SofPgFlt |
Rate of total page faults per CPU second |
|
State |
State of process |
|
BPri |
Base priority |
|
Ac |
Image activation flag, with 0 = no activation and 1 = activation |
|
Tm |
Image termination flag, with 0 = no termination and 1 = termination |
|
Privpgs |
Average count of private pages |
|
WSquo |
Working set quota |
|
Dirio/sec |
Direct I/O rate |
|
HrdPgFlt |
Rate of hard page faults per CPU second |
|
ImgActs |
Rate of image activations per second |
|
IBN |
Process type, with 0 = Interactive, 1 = Batch, and 2 = Network |
|
Li |
Login flag, with 0 = no login and 1 = login |
|
Lo |
Logout flag, with 0 = no logout and 1 = logout |
|
WSlist |
Average working set size |
|
WSext |
Working set extent |
|
DskIO/sec |
Disk I/O per second |
|
Dsk thpt |
I/O throughput in bytes per second |
|
Compct |
Percent of uptime in COM(O) state, sampled every 5 seconds |
|
AWSA |
Automatic working set adjustment flag, with 0 = AWSA enabled and 1 = AWSA disabled |
|
Top Dev |
Disk or tape drive with the highest operation rate from this process |
|
Top IO/Sec |
Operation rate per second, to the disk or tape drive with the highest operation rate, from this process |
|
2nd Dev |
Disk or tape drive with the second highest operation rate from this process |
|
2nd IO/Sec |
Operation rate per second, to the disk or tape drive with the second highest operation rate, from this process |
|
Tapio/sec |
Number of I/O operations per second that the process issued to tape devices |
|
Tap thpt |
Number of bytes per second transferred to and from tape devices for the process |
|
RespTim |
Response time. The time from the completion of a terminal input to the next terminal input or output or to the end of the interval or image termination. The unit of time is milliseconds. |
|
RespDur |
Response time in milliseconds. The time from the completion of a terminal input to the next terminal input or to the end of the interval or image termination. This response time plus think time equals 100% of the interval. |
|
RespWait |
Either the duration of response time that continues into the next interval (if PRO_M_RT_ENDS is set) or the duration of the most recently completed response time within the interval (if PRO_M_RT_ENDS is clear.) The unit of time is milliseconds. |
|
Trmio/sec |
Number of read I/O operations per second issued to the process's terminal. |
|
Trm thpt |
Number of characters per second read from the process's terminal (typing rate). |
|
Thnktim |
Think time. The time from the start of a terminal input to the completion of that terminal input or to the end of the interval or image termination. The unit of time is milliseconds. |
|
CmdWait |
Either the duration of think time that continues into the next interval (if PRO_M_TT_END is set) or the duration of the most recently completed think time within the interval (if PRO_M_RT_ENDS is clear). The unit of time is milliseconds. |
|
ProcType |
The process type indicates interactive, batch, network, detached, and/or subprocess. This hexadecimal number is derived from the value of the bits set for the process. Bit 0 interactive bit 3 detached bit 1 batch bit 4 subprocess bit 2 network For example, a value of 1 indicates an interactive process; a value of 12 (hex) indicates a process that is both a batch process and a subprocess. |
|
Copyright © 2008 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|