DataManager focuses on maintaining tables that contain input and output record definitions, abbreviated as IRDs and ORDs. These definitions describe every data item or field within each record.
Each record definition has a unique identifier called its name. Therefore, you refer to a specific record by specifying its IRD Name or ORD Name.
When an input file contains more than one kind of input record, DataManager needs to know how to differentiate them. That's the purpose of Input IDs. They tell DataManager how to recognize each type of record. For example, if an input data set contains three record types, all three IRD descriptions should include unique Input IDs. Each record description stores the unique value shared by all records of the same type and its location within the record.
Since DataManager outputs records for Performance Management and Accounting applications, duration of services is of primary importance. For this reason, every output record definition includes a header that specifies an ORD name, start stamp, stop stamp and duration.
Consist of date and time fields stored on the IRD. This information specifies when the process described by this record began and ended.
The name of an IRD field that specifies how long this process ran.
Some PMA applications require all their input records to have a unique identifier which is called a construct. One construct identifies all the input records for a single application. DataManager appends the construct to its output records.
Note: Only one construct is associated with each application, but output records can contain more than one construct. Therefore, an output record can be input to more than one PMA application.
The commit process takes the definitions you've been editing and makes them available for production runs. You only run the commit job when you want to "freeze" definitions you've been editing.
Input and output records you edit belong to the DEVELOPMENT version. When you commit records, their version changes:
Having two versions of committed output definitions allows you to work in two different environments: test and production. The PROD version allows you to keep running daily production jobs while the TEST version lets you test out changes you've made to the production version.
Input Tables Output Tables ________________ ________________ | DEVELOPMENT | | DEVELOPMENT | | version |<──── records you edit ────>| version | | records | | records | ________________ ________________ | REAL version |<──── records CA PMA/DM ┌──>| TEST version | | records | processes | | records | ________________ | ________________ └──>| PROD version | | records | ________________
The CAIKSPAR file contains information about the database system you use, along with specific DataManager and CA PMA Chargeback parameters. Both products use the CAIKSPAR file for batch processing and online sessions. DataManager accesses CAIKSPAR for all types of processing:
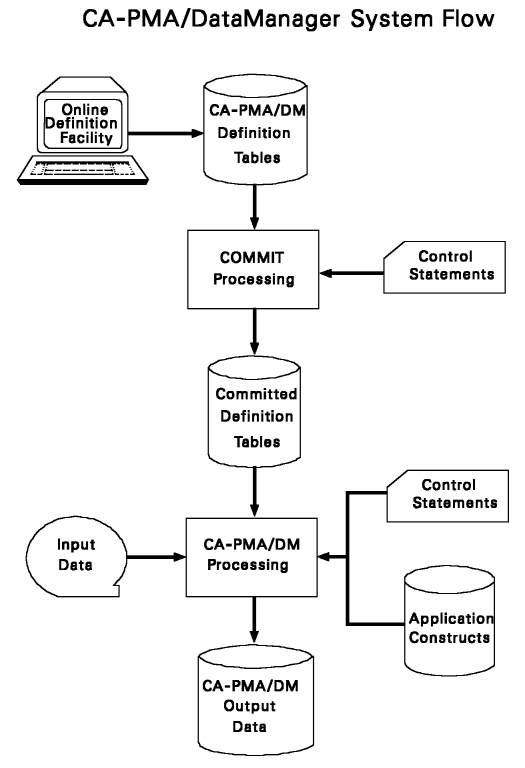
Once input data is processed by DataManager, it is ready for use by PMA applications.
| Copyright © 2012 CA. All rights reserved. |
|