

The following diagram is an overview of the OM Web Services that shows how data flows into the Web Service, is processed and then returned:
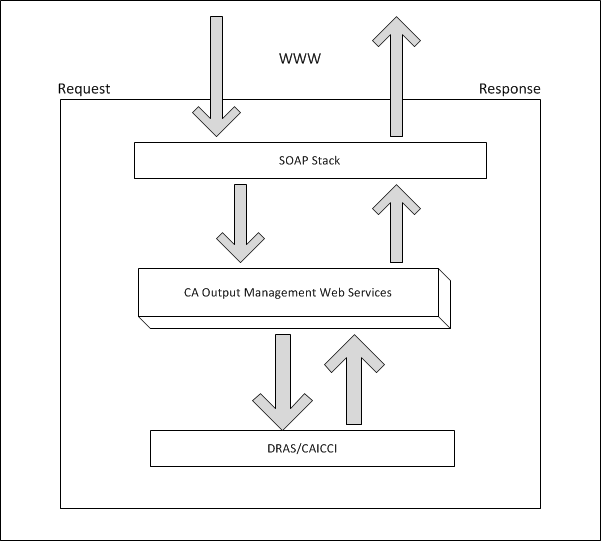
Note: For each Web Service API call, an individual DRAS connection is created. A DRAS connection will be established to execute each API call and be disconnected after the call, which can incur a significant performance overhead.
To reduce the connection cost, a local cache method is recommended to store the returned report lists and report data in the local memory of the Web Service client applications. Depending on the timeliness of your application data, you can construct this cache to be refreshed periodically.
Note: For more information, see Terms Used in this Guide.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|