The SYSCMD facility gives you the ability to issue operating system commands and receive responses without having to use a real operating system console; for example, to display the channel path or unit status of a local non-SNA terminal.
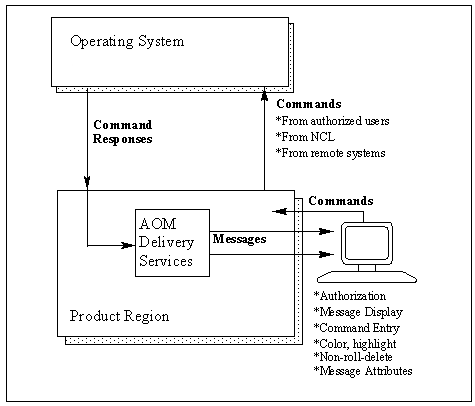
The SYSCMD command has several operands that you can use to enter master console commands, lock a console, or issue a command as if it came from a specific console.
In its most basic form, the SYSCMD command is:
SYSCMD command-text
The command to be entered.
Note: You are restricted in your use of the SYSCMD facility by both your command authority and your user security profile. These are set by your systems administrator.
If the command to be entered is usually restricted to the master console, the CON=MASTER operand must be used with the SYSCMD command.
Example
SYSCMD CON=MASTER DATA=VARY CPU(0) OFFLINE
You must have MASTER authority for this.
Note: This is not necessary if you are using Extended Multiple Console Support (EXTMCS) consoles.
To ensure that you can issue commands when you need to, you can lock a console to a specific environment using the following operand:
OPT=LOCK
When you no longer require the console, you should release it, using the following operand, so that it is made available to other SYSCMD users:
OPT=REL
If you want to simulate issuing a command from a specific console that you are not using, enter the following form of the SYSCMD command (where n is the console number):
SYSCMD CON=n DATA=command-text
This can be done from anywhere in the system.
As no console authority checks are made by the SYSCMD facility, the existing authority for the specified console is used.
Note: The form of the SYSCMD command described in the example above is not supported if you are using EXTMCS consoles.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. |
|