

The maximum number of symbols-such as names and identifiers-in a CA Ideal application depends greatly on the amount of storage CA Ideal has available for the Field Attribute Table and the Symbol Table.
The Field Attribute Table, referred to here as the FAT, contains an entry for each dataview, dataview field, panel, panel field, working data field, literal, and FOR construct. Each entry is 20 bytes long and contains information such as the length, type, displacement, and the offset into the Symbol Table.
The Symbol Table contains an entry for each dataview name, dataview field name, panel name, panel field name, working data field name, report name, procedure name, and label name. The length of these entries varies according to the length of the symbol. Each entry contains information, such as the length of the symbol and the address of the symbol in the FAT, and the literal that identifies the symbol.
During compilation, CA Ideal creates a variety of blocks. None of these blocks can exceed 32 KB. If all the FAT or Symbol Table entries of a 01 level cannot fit in the remaining space of the current block, a new block is started. No parent (01 level) is separated from its children. The FAT and Symbol Table can span multiple blocks.
A single data entity occurrence, (which means that a 01 level data item, dataview, or panel), still cannot exceed the 32 KB limit.
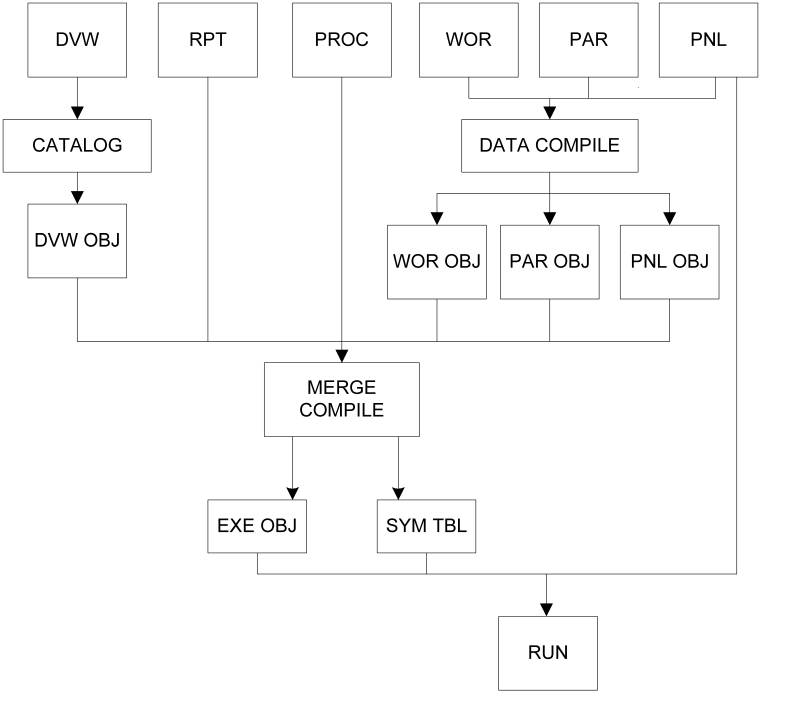
This means that no 01 level can have more than 1,600 fields, or it exceeds the FAT table limit. Also, the maximum that a 01 level can have is somewhere between 800 and 1,875 fields (depending on the size of the symbols), otherwise it exceeds the Symbol Table limit. The compilation and execution process is shown in the following illustration.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|