

There are several different types of orders for software delivery purposes, including:
Distribute registered items and item procedures from the Software Package Library on the enterprise manager to the domain manager libraries. The item registration orders include the library item and its registration information files.
To be distributed from a domain manager, software programs must be registered in the Software Package Library on the domain manager. You can also create new versions of software packages and make use of the delta delivery mechanism; that is, only distribute the files that are different from the previously distributed version.
Install or uninstall a program on a computer or computer group.
Retrieve a specific file or files from the domain managers to a designated place on the enterprise manager.
Deregister and delete items from a domain manager's Software Package Library or computer groups. When a program is deregistered and deleted, all associated item procedures (both embedded and added) are deregistered as well.
Items from the Software Package Library on a domain manager can only be deregistered and deleted, if they were initially distributed from the enterprise manager, and have not been installed on a computer at the domain.
Initiate the program itself. For example, an activation order can be used to trigger the start of an archive program on a remote computer.
Initiate changes in the configuration files on a remote computer. Configuration type tasks are defined as item procedures.
Register and deregister software policies on domain managers.
Purge software and set as archived on the domain managers' libraries; for example, software not frequently used. This is useful to preserve disk space. The software can be restored on demand.
The following illustration shows the flow of orders from the enterprise manager to the domain manager (using distribution containers) and from the domain manager to the target computers (using job containers).
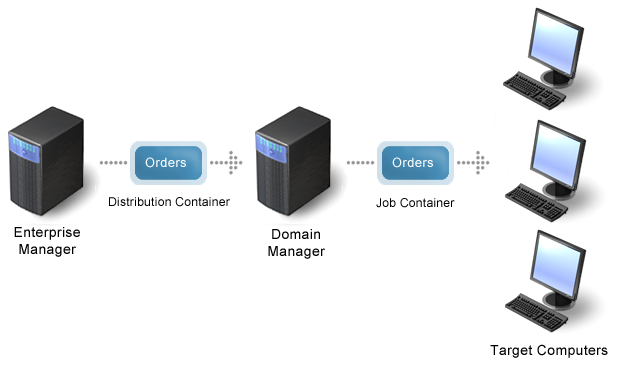
Once jobs are delivered to the target computer, the software delivery (SD) manager or the SD agent can initiate job execution on the target computer.
Orders can include a trigger so that the SD manager initiates job execution. In the absence of a trigger, the agent uses Job Check to contact the manager and initiate job execution. Orders are queued until Job Check checks for held orders. The frequency, with which that check occurs depends on the Job Check options available to the operating system under which the targeted computer is running.
Item procedures carry orders to install, uninstall, activate, and configure items on target computers. When an order is received and activated, it proceeds as if the item procedure was initiated directly on that computer.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|