

Type-specific rights are rights that affect specific object types only, such as Crystal Reports, folders, or access levels.
Type-specific rights consist of the following:
These rights are identical to general global rights (for example, the right to add, delete, or edit an object), but you set them on specific object types to override the general global rights settings.
These rights are available for specific object types only. For example, the right to export a report's data appears for Crystal Reports but not for Word documents.
The diagram Type-specific rights example illustrates how type-specific rights work. Here right 3 represents the right to edit an object. Blue Group is denied Edit rights on the top-level folder and granted Edit rights for Crystal Reports in the folder and subfolder. These Edit rights are specific to Crystal Reports and override the rights settings on a general global level. As a result, members of Blue Group have Edit rights for Crystal Reports but not the other object type in the subfolder.
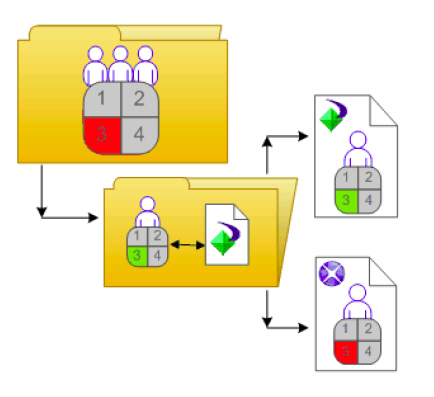
Type-specific rights are useful because they let you limit the rights of principals based on object type. Consider a situation in which an administrator wants employees to be able to add objects to a folder but not create subfolders. The administrator grants Add rights at the general global level for the folder, and then denies Add rights for the folder object type.
Rights are divided into the following collections based on the object types they apply to:
These rights affect all objects.
These rights are divided according to particular content object types. Examples of content object types include Crystal Reports, Adobe Acrobat PDFs, and Desktop Intelligence documents.
These rights are divided according to which BusinessObjects Enterprise application they affect. Examples of applications include the CMC and InfoView.
These rights are divided according to which core system component they affect. Examples of core system components include Calendars, Events, and Users and Groups.
Type-specific rights are in the Content, Application, and System collections. In each collection, they are further divided into categories based on object type.
|
Copyright © 2010 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|