

Rights override is a rights behavior in which rights that are set on child objects override the rights set on parent objects. Rights override occurs under the following circumstances:
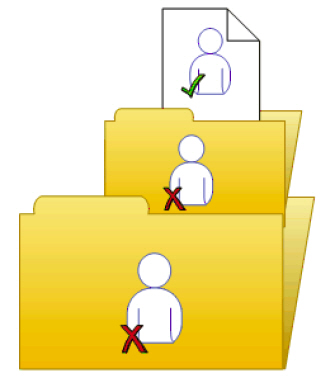
You do not need to disable inheritance to set customized rights on an object. The child object inherits the rights settings of the parent object except for the rights that are explicitly set on the child object. Also, any changes to rights settings on the parent object apply to the child object. Rights override example 1 illustrates how rights override works on parent and child objects. Blue User is denied the right to edit a folder's contents; the rights setting is inherited by the subfolder. However, an administrator grants Blue User Edit rights to a document in the subfolder. The Edit right that Blue User receives on the document overrides the inherited rights that come from the folder and subfolder.
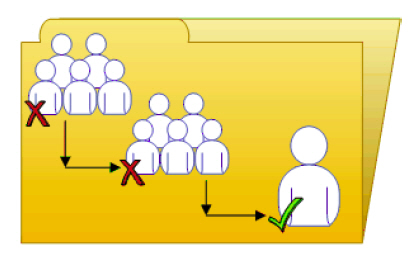
Rights override example 2 illustrates how rights override works on members and groups. Blue Group is denied the right to edit a folder; Blue Subgroup inherits this rights setting. However, an administrator grants Blue User, who is a member of Blue Group and Blue Subgroup, Edit rights on the folder. The Edit rights that Blue User receives on the folder override the inherited rights that come from Blue Group and Blue Subgroup.
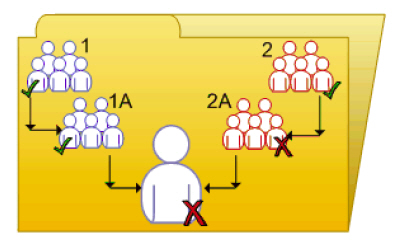
Complex rights override illustrates a situation where the effects of rights override are less obvious. Purple User is a member of subgroups 1A and 2A, which are in Groups 1 and 2, respectively. Groups 1 and 2 both have Edit rights on the folder. 1A inherits the Edit rights that Group 1 has, but an administrator denies Edit rights to 2A. The rights settings on 2A override the rights settings on Group 2 because of rights override. Therefore, Purple User inherits contradictory rights settings from 1A and 2A. 1A and 2A do not have a parent-child relationship, so rights override does not occur; that is, one sub-group's rights settings do not override another's because they have equal status. In the end, Purple User is denied Edit rights because of the denial-based rights model in BusinessObjects Enterprise.
Rights override lets you make minor adjustments to the rights settings on a child object without discarding all inherited rights settings. Consider a situation in which a sales manager must view confidential reports in the Confidential folder. The sales manager is part of the Sales group, which is denied access to the folder and its contents. The administrator grants the manager View rights on the Confidential folder and continues to deny the Sales group access. In this case, the View rights granted to the sales manager override the denied access that the manager inherits from membership in the Sales group.
|
Copyright © 2010 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|