

Networks are created when one record type is a member of more than one set. Multiple membership logically relates the owner records of two (or more) sets that have common members. An owner record of the first set type is related to many members. Each of these members is related to an owner of the second set type. This creates a one-to-many relationship between the owners of the first set type and owners of the second set type. Since the logic applies equally in reverse, we have a many-to-many relationship between the two owner types.
In our example, the EMPOSITION record type at Commonweather Corporation is owned by both the EMPLOYEE and JOB record types. The following diagram illustrates this example of multiple membership for June Moon, John Done, Peter Plum, and the four project positions to which they are assigned.
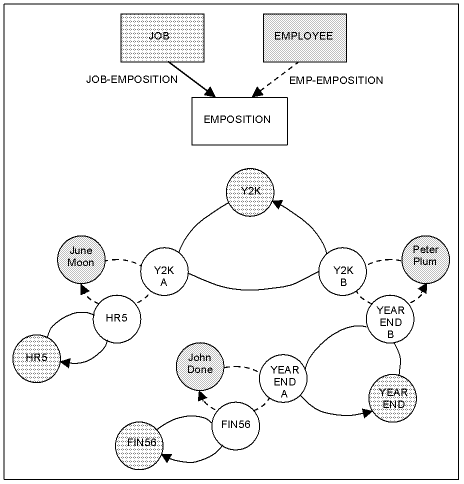
We can use this example to determine who is assigned to the Y2K project by answering the following questions:
Question: What are the members of the JOB-EMPOSITION set when Y2K is the owner?
Answer: Y2K-A and Y2K-B.
Question: Which record owns the EMP-EMPOSITION set occurrence when Y2K-A is a member? When Y2K-B is a member?
Answer: John Done and June Moon.
A record type can be a member of an unlimited number of sets. This allows the representation of complex interrelationships within a database without replicating data.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|