

CA IDMS scratch management functions allow you to allocate, retrieve, and delete scratch records. Scratch records, which are stored in the DDLDCSCR area of the dictionary, are used to pass data from one task to subsequent tasks running on the same terminal. These records are not accessible to tasks executing on other terminals.
Fast Access
Scratch records provide fast access because:
Best Use of Scratch Records
Scratch records are not recoverable across a shutdown/startup or a system crash. All scratch records are deleted at system startup. Because they are not saved across a system shutdown, scratch records are best used for temporary storage of data.
Availability to a Subsequent Task
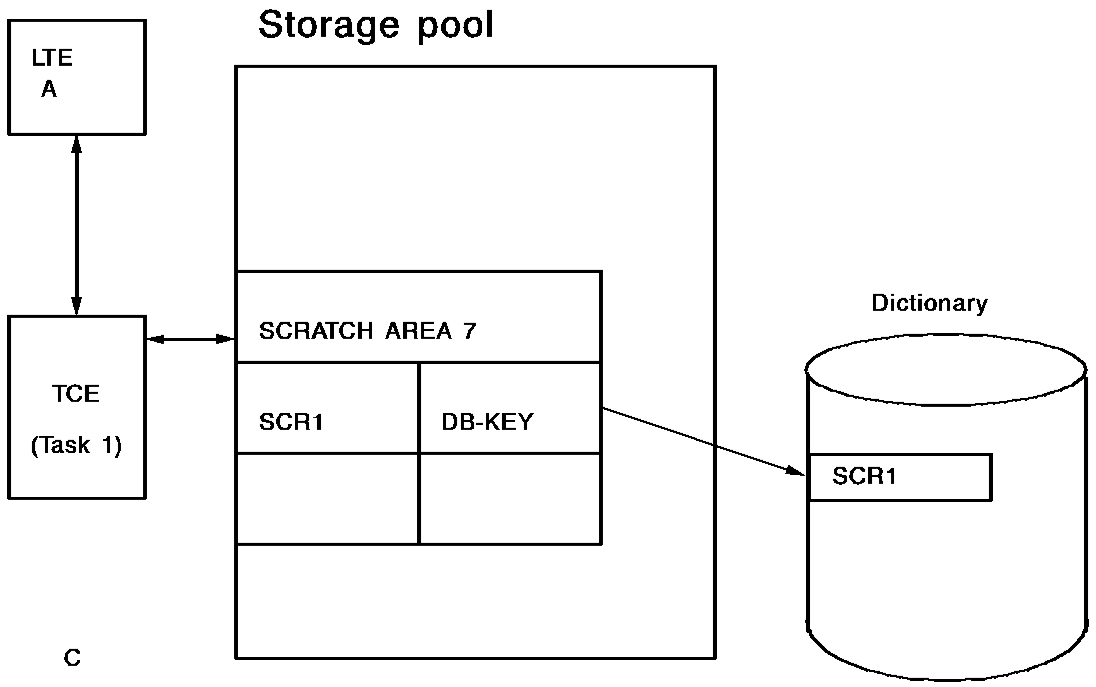
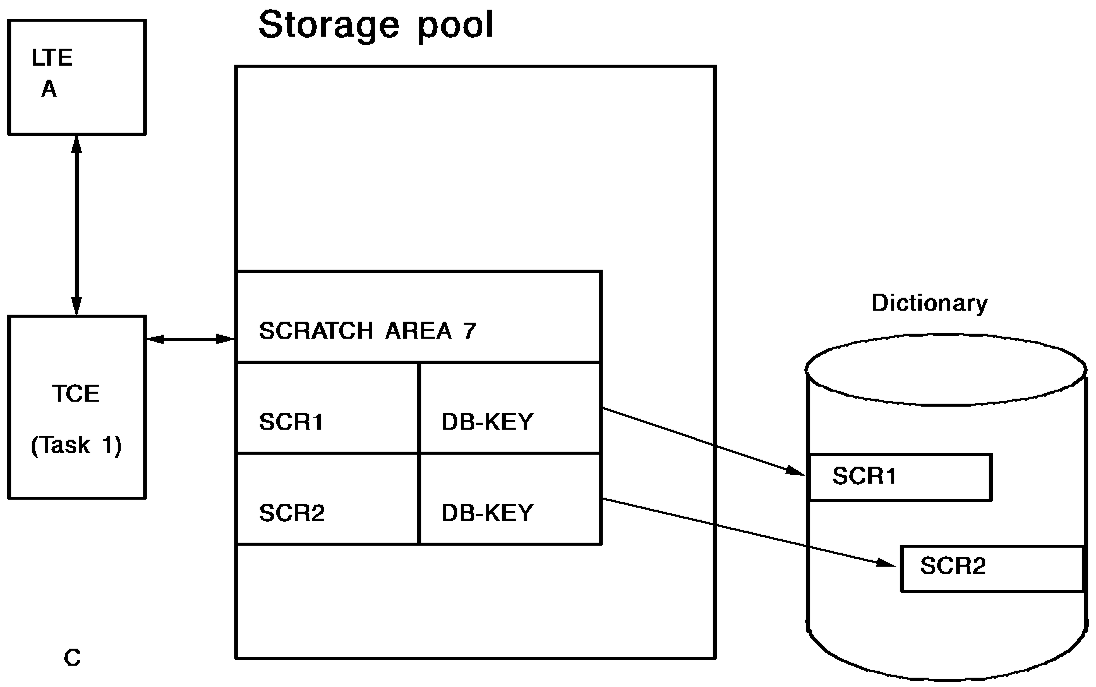
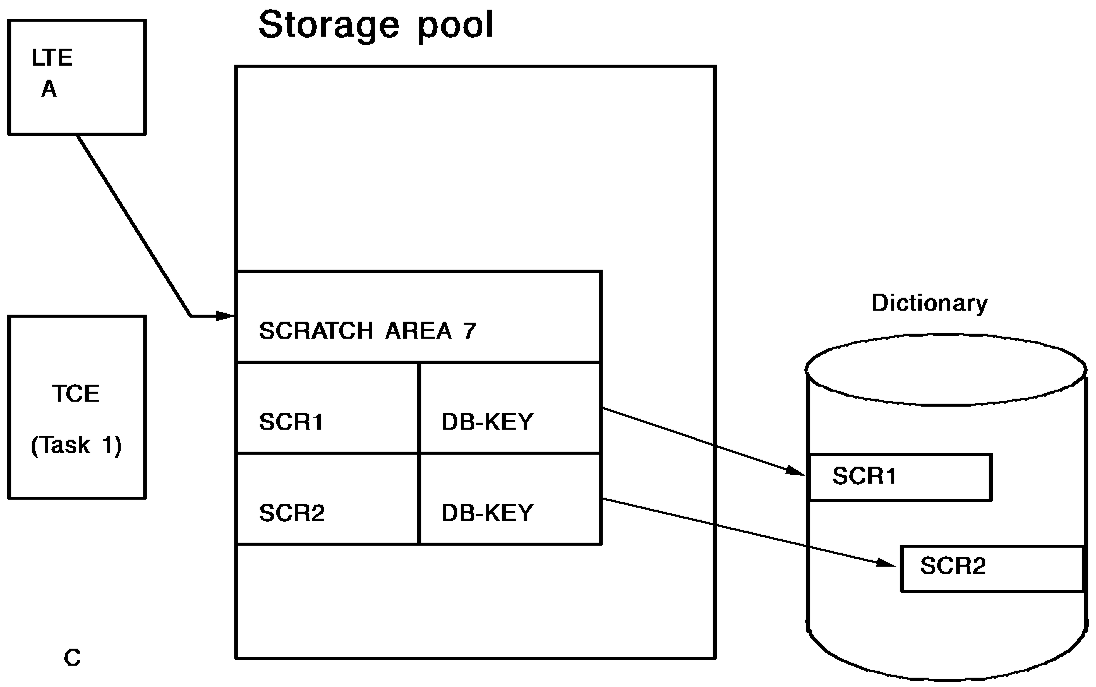
When a task terminates, CA IDMS temporarily associates that task's scratch areas with the logical terminal from which the task was invoked. This is done using the logical terminal element (LTE). When a new task is initiated on the same terminal, CA IDMS transfers the scratch areas to the task control element (TCE) for the new task. All scratch records and currencies associated with the old task are available to the new task.
What You Can Do with Scratch Records
You can use CA IDMS scratch management functions to do the following:
Steps to Allocate or Replace a Scratch Record
To allocate or replace a scratch record, perform the following steps:
Scratch Area
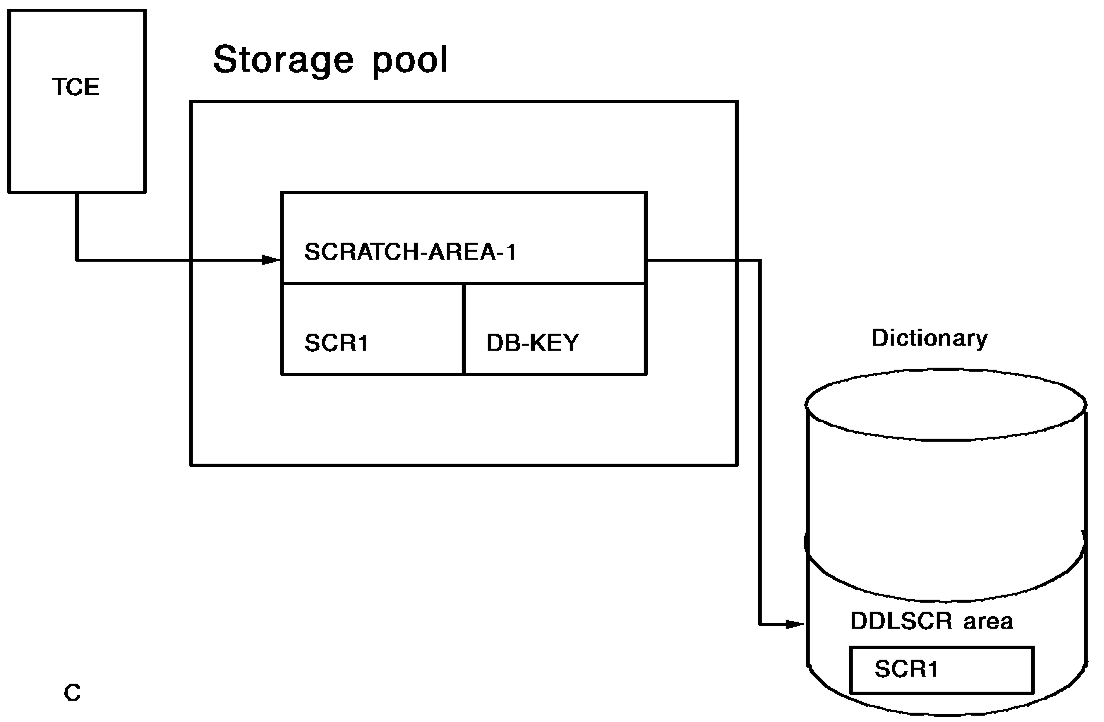
In response to your PUT SCRATCH request, CA IDMS places the scratch record in the DDLDCSCR area of the dictionary. An index pointer to the record is placed in a storage pool scratch area. Each scratch area is identified by its area ID; scratch records in each area are indexed in ascending order by scratch record ID (SRID).
Typically, your program assigns the SRID. If not, CA IDMS assigns the SRID, places the record last within the scratch area, and returns the SRID to your program.
Any number of scratch areas can be associated with a task and any number of scratch records can be associated with a scratch area.
Example of Scratch Record Allocation
The figure below shows scratch record allocation. When a PUT SCRATCH request is issued, CA IDMS creates a scratch record in the dictionary and places a pointer to that record in a scratch area associated with the issuing task.
Steps to Retrieve a Scratch Record
To retrieve a scratch record, perform the following steps:
If there is any chance that the length of the retrieved record exceeds the length of its allocated variable storage, you should do the following:
Include the KEEP parameter of the GET SCRATCH statement to ensure that data is not deleted when it is retrieved.
'Scratch record currency'. CA IDMS maintains currency for the records in each scratch area. Because CA IDMS maintains currency across tasks, you should be aware that the NEXT option does not default to FIRST, and PRIOR does not default to LAST.
Steps to Delete a Scratch Record
To delete a scratch record, issue either of the following commands:
The following diagrams illustrate how CA IDMS dynamically allocates scratch records across tasks:
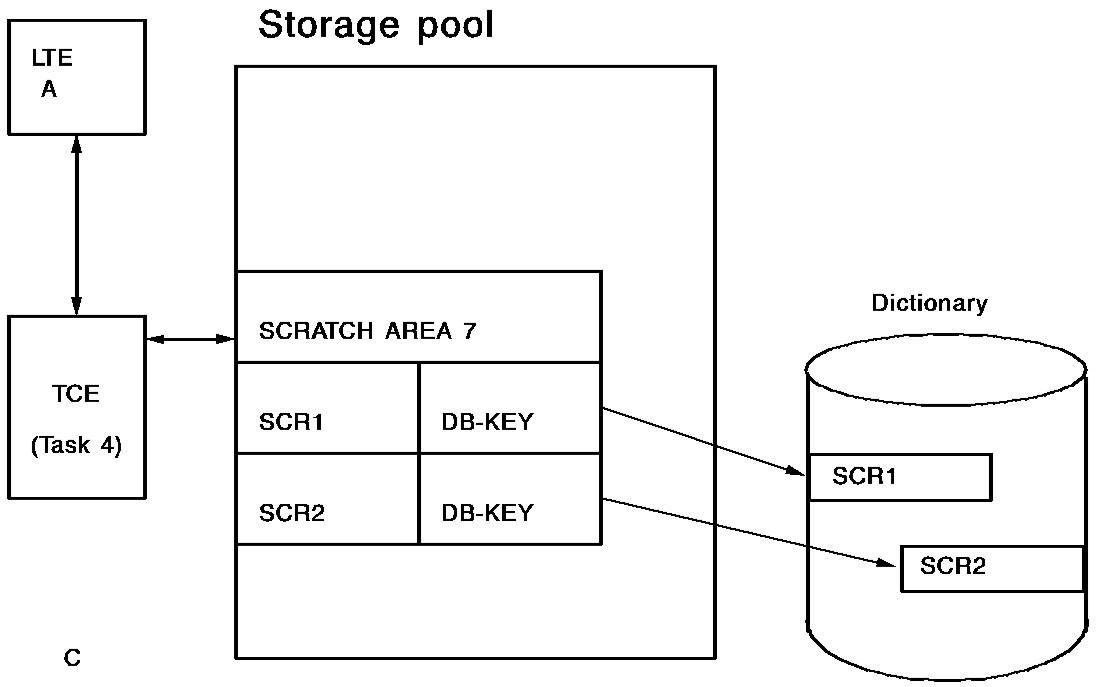

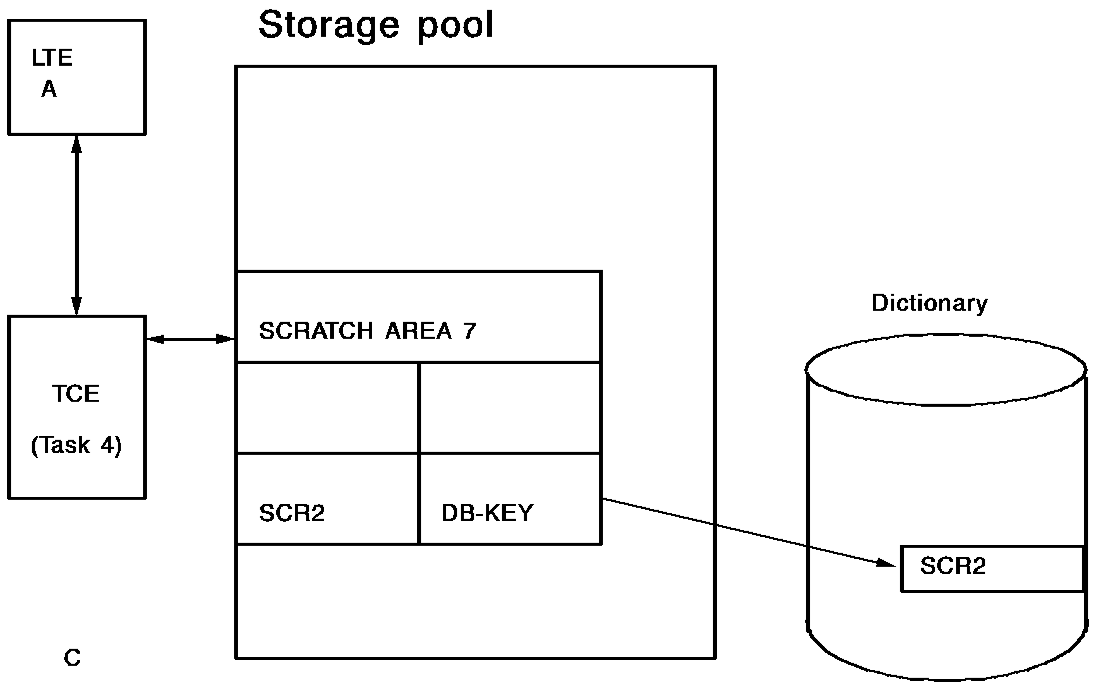
Example of Retrieving Scratch Records
The program excerpt below retrieves scratch records from the TEST-SCRATCH scratch area. The program uses a pageable map in order to display an unlimited number of scratch records.
The program retrieves all occurrences in the TEST-SCRATCH scratch area. Each occurrence contains the employee's ID, last name, and first name.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 TC PIC X(8).
88 GETOUT VALUE 'GETSCR2'.
01 SWITCHES.
05 FIRST-PAGE-SW PIC X VALUE 'N'.
88 LESS-THAN-A-PAGE VALUE 'N'.
01 GETSCR2 PIC X(8) VALUE 'GETSCR2'.
01 TESTSCR PIC X(8) VALUE 'TESTSCR'.
01 TEST-SCRATCH.
05 SCR-ID PIC 9(4).
05 SCR-LNAME PIC X(15).
05 SCR-FNAME PIC X(10).
05 TEST-SCRATCH-END PIC X.
01 SCRMAP-REC.
02 ID PIC 9(4).
02 LNAME PIC X(15).
02 FNAME PIC X(10).
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-LINE.
ACCEPT TASK CODE INTO TC.
IF GETOUT ENDPAGE
DC RETURN.
BIND MAP SCRMAP01.
BIND MAP SCRMAP01 RECORD SCRMAP-REC.
STARTPAGE SESSION SCRMAP01 NOWAIT BACKPAGE BROWSE
ON DC-SECOND-STARTPAGE NEXT SENTENCE.
*
GET SCRATCH AREA ID TESTSCR FIRST KEEP
INTO TEST-SCRATCH TO
TEST-SCRATCH-END
ON DC-AREA-ID-UNK
GO TO ERR-NO-SCR.
MOVE SCR-ID TO ID.
MOVE SCR-LNAME TO LNAME.
MOVE SCR-FNAME TO FNAME.
MAP OUT USING SCRMAP01
DETAIL NEW.
PERFORM A100-GET-SCRATCH THRU A100-EXIT
UNTIL DC-REC-NOT-FOUND.
IF LESS-THAN-A-PAGE
MAP OUT USING SCRMAP01
NEWPAGE RESUME.
DC RETURN NEXT TASK CODE GETSCR2.
A100-GET-SCRATCH.
GET SCRATCH AREA ID TESTSCR NEXT KEEP
INTO TEST-SCRATCH TO
TEST-SCRATCH-END
ON DC-REC-NOT-FOUND GO TO A100-EXIT.
MOVE SCR-ID TO ID.
MOVE SCR-LNAME TO LNAME.
MOVE SCR-FNAME TO FNAME.
MAP OUT USING SCRMAP01
DETAIL NEW
ON DC-FIRST-PAGE-SENT
MOVE 'Y' TO FIRST-PAGE-SW.
A100-EXIT.
EXIT.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|