

Physical area locks
CA IDMS/DB examines and sets physical area locks whenever an area is opened in an update mode. Physical area locks:
Physical locks are handled differently depending on the mode of processing:
If the lock is removed after system startup, the operator must vary the area status from offline to online to make the area available to the central version.
Logical area locks
Logical area locks are used by central version to control concurrent access to areas by database transactions running under central version. Logical area locks are derived from the mode in which an area is readied. A logical lock on a database area sometimes causes transactions to wait for database resources. When a transaction cannot ready an area because of a protected or exclusive restriction placed on that area by another transaction, the second transaction is placed in a wait state until the first transaction is finished.
Concurrent area access
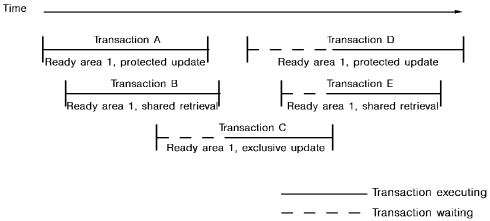
The following diagram shows the way in which ready modes and ready options restrict concurrent use of an area by database transactions executing under one central version.
Transaction A readies AREA1 in protected update mode; transaction B readies the area in shared retrieval mode; and transaction C attempts to ready the area in exclusive update mode and is put into a wait state until both transactions A and B terminate. Transactions D and E, attempting to ready the area, must wait until transaction C terminates.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|