

Conserving disk space
To conserve disk space, you can instruct the database to compress data before storage and decompress it after retrieval. There are three ways to compress and decompress data:
These procedures are invoked automatically by the DBMS as data is stored and retrieved.
Note: Only CA IDMS Presspack is available for SQL-defined data.
Advantages and disadvantages of data compression
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of data compression.
|
Efficiency Considerations |
Potential Impact |
|---|---|
|
I/O |
By compressing an entity, you conserve storage resources, allowing the system to fit more entities on each database page. If you can fit all entity occurrences associated through a particular relationship on a single page, the system will only perform one I/O to access these entities. |
|
CPU time |
Compressing data requires some extra CPU time to perform compression/decompression processing. |
|
Space management |
Compression can be used to conserve considerable amounts of storage. |
|
Contention |
No difference. |
Considerations for using CA IDMS Presspack
CA IDMS Presspack uses Huffman techniques to compress database entities. The techniques include assigning unique bit string codes of different lengths to single character and character strings. These codes substitute for the character and character strings in the entities.
To assign the codes, CA IDMS Presspack uses character and character-string frequencies of occurrence. It assigns shorter codes to the most frequently occurring characters and character strings. To those that occur less frequently, CA IDMS Presspack assigns longer codes.
CA IDMS Presspack compresses both textual and nontextual data.
For further information about CA IDMS Presspack, see CA IDMS Database Administration Guide and CA IDMS Presspack User Guide.
Considerations for using IDMSCOMP and IDMSDCOM
IDMSCOMP and IDMSDCOM are supplied with CA IDMS/DB. They are placed in the load (core-image) library at installation time and are also provided in source form so you can modify them if necessary. You can also write your own database procedure or use other commercially available compression/decompression procedures.
For further information about database procedures, see CA IDMS Database Administration Guide.
To compress data, IDMSCOMP performs the following conversion procedures:
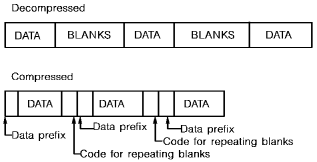
Data that does not fall into any of the above categories remains unchanged. Each group of unchanged data is prefixed by a 2-byte code. The following diagram shows the compression of contiguous blanks in an entity.
Considerations for user-written procedures
If writing your own compression procedures, you must follow conventions for writing database procedures.
For information on database procedures, see CA IDMS Database Administration Guide.
Guidelines for compression
Consider the following guidelines when deciding whether data should be compressed:
The control portion of an entity includes all data elements up to the last key (CALC, sort, index). Since this portion of an entity is not compressible, it may mean that not enough compressible data exists to justify compression.
Storage mode
If you decide to compress data in an entity, you should add a storage mode of C for the entity on the data structure diagram.

|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|