

To connect new members to indexed sets with FIRST, LAST, NEXT, and PRIOR set order, CA IDMS/DB inserts a new index entry between existing index entries. When one SR8 record fills, CA IDMS/DB creates a new SR8 record; there is only one level of SR8 records in an unsorted index.
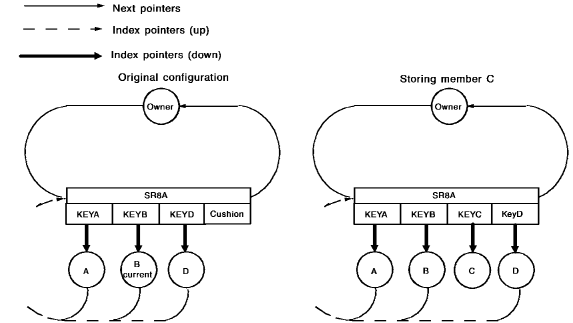
Once a request has been made to connect a member occurrence to an indexed set, CA IDMS/DB first checks whether other entries exist. If no other entries exist, CA IDMS/DB creates and stores the first SR8 record (containing the first entry) and connects it to the owner occurrence with next, prior, and owner pointers. The target page for the first SR8 record is the page of the owner of the indexed set occurrence (plus displacement, if any).
CA IDMS/DB Actions
If other entries do exist, CA IDMS/DB takes the following actions:
Step 1
Identifies the appropriate SR8 record and insertion point based on the set order, as follows:
Note: SQL-defined unsorted indexed constraints have an internal order of LAST.
Step 2
Inserts the new entry into the index, as follows:
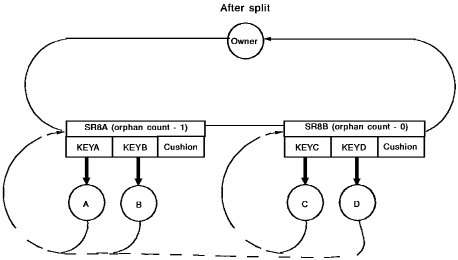
Index Pointers for Split SR8s
When CA IDMS/DB splits an SR8 record (Record A) into two SR8 records (Records A and B), the entries relocated to Record B point to member occurrences that still contain index pointers pointing to Record A if index pointers are maintained for the set (index pointers are optional for system-owned indexes). If index pointers are maintained, splitting Record A causes CA IDMS/DB to set the orphan count in Record A equal to the number of entries moved to Record B.
Splitting an SR8 Record
The following diagram shows splitting an SR8 record to add a member occurrence to an indexed set with a set order of NEXT. (Note that, for simplicity, prior and owner pointers are not included in this figure.)
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|