

Pointers Deleted
To avoid consuming unnecessary time and I/O disconnecting records from sets without prior pointers, CA IDMS/DB does not physically delete the record when an ERASE command is issued. Instead, the next time CA IDMS/DB encounters a logically deleted record while walking a chained set of which the record is a member, CA IDMS/DB disconnects the record from the set, provided that the record's area was readied in update mode. Since the record prior to the logically deleted record is still current of run unit, CA IDMS/DB can update the record's next pointer and disconnect the logically deleted record. To be physically deleted, the record must have been disconnected from all sets in which the record was a member.
Operations Performed
CA IDMS/DB performs the following operations to logically delete a record:
Example
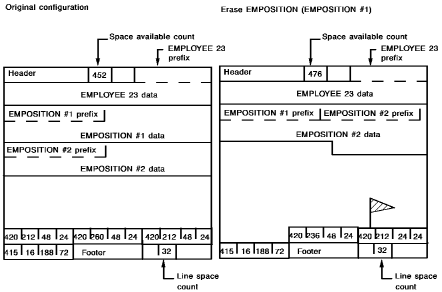
In the following example, assume that the EMPOSITION records do not have prior pointers in the EMP-EMPOSITION set. When erasing an EMPOSITION record, CA IDMS/DB removes only the data and flags the record's line index. The EMPOSITION record is logically deleted. The next time CA IDMS/DB is walking this occurrence of the EMP-EMPOSITION set in update mode and encounters the flagged record, CA IDMS/DB physically deletes the record.
Consideration
Occasionally, in recovering from an error during a store operation, CA IDMS/DB may create a logically deleted record. If CA IDMS/DB has stored a record and is in the process of making the automatic connections when CA IDMS/DB discovers an error condition (for example, no currency established in one of the automatic sets), CA IDMS/DB must erase the record being stored. If one of the chained sets to which the record has already been connected has next pointers only, CA IDMS/DB logically deletes the record.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|