

Storage Strategy
If a record has a storage mode of VIA a chained set (or CLUSTERED around a referential constraint), CA IDMS/DB uses the location of the current record of set (always the referenced row of referential constraints) to determine where to store the new record, as follows:
|
If the members and owners in the specified set are assigned to the same page range, and if you have not specified displacement in the non-SQL schema... |
CA IDMS/DB stores the member record occurrence as close as possible to the owner |
|
If the members and owners in the specified set are assigned to the same page range, and you have specified displacement in the non-SQL schema... |
CA IDMS/DB stores the member record occurrence as close as possible to the owner, allowing for displacement |
|
If the members and owners in the specified set are assigned to different page ranges... |
CA IDMS/DB stores the member record occurrence as close as possible to the page (within the member record's page range) that is proportional to the location of the owner (within the owner's page range) |
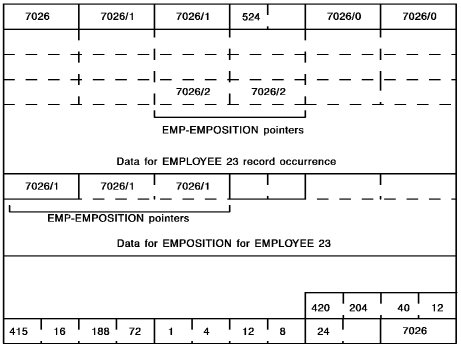
The following diagram shows how CA IDMS/DB stores a record through a chained set. For a discussion of how CA IDMS/DB stores a record through an indexed set, see 36.1.2.2, “Storing records via an indexed set”.
Example
In this example, EMPLOYEE 23 has randomized to page 7026. EMPLOYEE 23's EMPOSITION record is stored VIA EMPLOYEE 23 on page 7026. To locate the EMPOSITION record, CA IDMS/DB applies the randomizing routine to EMPLOYEE 23 (giving page number 7026), enters page 7026 on the SR1 record, and follows the CALC set until the EMPLOYEE 23 record is located. CA IDMS/DB then obtains the EMPOSITION record through the EMP-EMPOSITION chain.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|