

Space Management › Database Pages
Database Pages
Size of Database
A database can have from 2 to 1,073,741,822 pages. Each area contains pages of equal size. Each page can contain up to 32,756 bytes of data. For details, see 35.3, “Database Keys". Database pages are mapped to BDAM, or DAM blocks, or VSAM control intervals (for details, see Chapter 17, “Allocating and Formatting Files"). Each database page is identified by a unique page number and data transfers are accomplished one page at a time.
Page Format
All database pages, regardless of size, have a header and footer with the same general format as shown in the following diagram. A database page always has a header at the beginning of the page and a footer at the end; free space is in the middle.
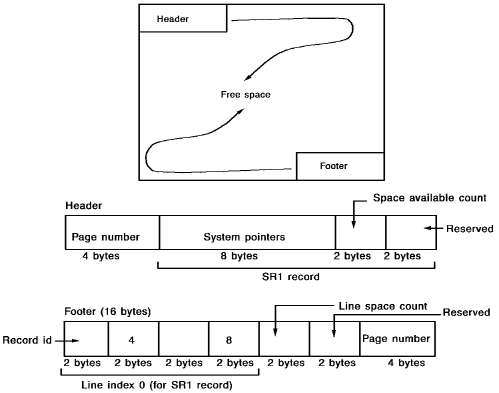
Header
The header occupies the first 16 bytes of each page and is formatted as follows:
- Page number (4 bytes)—A unique, system-assigned number of the page.
- SR1 system record (12 bytes)—An SR1 record is stored on each page during initialization by the FORMAT utility. Each SR1 record contains the space available count (that is, the number of bytes of free space on the page).
Footer
The footer occupies the last 16 bytes of each page and is formatted as follows:
- Line index 0 (8 bytes)—Identifies the location and length of the SR1 system record
- Line space count (2 bytes)—Number of bytes used for line indexes and the footer
- Filler (2 bytes)—Reserved space
- Page number (4 bytes)—The unique system-assigned number of the page
Note: Numeric fields maintained by CA IDMS are in binary format, although this manual represents them as decimal numbers.
To simplify the illustrations, the page size (800 bytes) in the figures of this manual is unusually small.
Database Page Layout
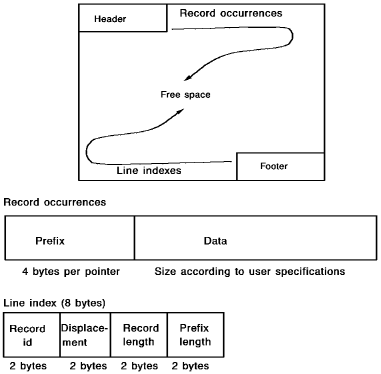
Except for the header and the footer, pages are filled with the following entries:
- Record occurrences—The actual record occurrences are positioned on the page from top to bottom immediately following the header. Each occurrence consists of a prefix (containing pointers) and a data portion. A page can hold from 3 to 2,727 record occurrences depending on user specification (for details, see 35.3, “Database Keys".)
- Line indexes—The line indexes identify the locations of record occurrences on the page and are positioned on the page from bottom to top, immediately preceding the footer. A page contains one line index per record occurrence on the page. Each line index has the following format:
- Record id (2 bytes)—Identification of the record type
- Displacement (2 bytes)—Location of the record occurrence relative to the beginning of the page, where the first byte on the page is position 0
- Record length (2 bytes)—Length of the entire record occurrence stored on this page (data plus prefix) in bytes
- Prefix length (2 bytes)—Length of the prefix portion of the record in bytes
Record occurrences are added from the top down; line indexes from the bottom up. Free space is always in the middle.
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|



