

Loading SQL Defined Databases
CA IDMS provides utilities to efficiently load a database that has been defined with SQL DDL statements. The entire load operation can be performed as a single operation using the LOAD utility statement, or it can be executed as separate operations using a combination of the LOAD, BUILD, and VALIDATE utility statements. Regardless of which method is used, loading an SQL-defined database consists of multiple phases and steps within those phases.
Loading Phases
The following table summarizes the phases involved with loading an SQL-defined database. The load process was designed to accommodate both small databases and very large databases and allow flexibility in tailoring the load process to the characteristics of the data being loaded:
|
Phase |
What it does |
|---|---|
|
Load |
Loads the specified tables |
|
Build |
Builds indexes and linked index constraints for the specified tables; this phase can be bypassed if neither linked index constraints nor non-clustering indexes are defined on the specified tables |
|
Validate |
Validates referential constraints in which the specified tables participate |
Steps Within Phases
Each of these phases, in turn, is composed of sub-phases called steps. The following table summarizes the function of each step:
|
Phase |
Step |
What it does |
|---|---|---|
|
Load |
Step 1 |
Processes data in preparation for sorting; this step can be bypassed if data is already sorted |
|
|
Step 2 |
|
|
Build |
Step 1 |
Performs an area sweep in the absence of an intermediate extract file |
|
|
Step 2 |
Finds the db-keys of rows that participate in the referenced table of a linked index referential constraint |
|
|
Step 3 |
Builds non-clustering indexes and linked indexes |
|
|
Step 4 |
Updates the prefixes of rows that participate as the referencing table of a linked index referential constraint |
|
Validate |
Step 1 |
Validates only those constraints that can be processed efficiently in a single pass and extracts information about other referential constraints |
|
|
Step 2 |
Validates any referential constraints bypassed in Step 1 |
Loading Options
CA IDMS/DB offers you the following loading options:
|
Option |
Description |
When to use it |
|---|---|---|
|
Full load |
Loads, builds and validates the specified tables |
Always, unless special considerations apply |
|
Phased load |
Executes each phase (load, build, and validate) separately |
When loading a number of tables one at a time or in groups; defer build and validate phases until all the tables have been loaded |
|
Segmented load
|
Loads portions of input in separate operations |
When loading extremely large tables; defer the build and validate steps until all the input records have been processed |
|
Stepped load
|
Executes each step of a phase (load, build, and validate) separately |
When loading extremely large tables for which external sort packages may be more efficient or when space for intermediate work files or tape drives is at a premium |
Load Flow Diagram
The following diagram illustrates the load and build phases of the process described above:
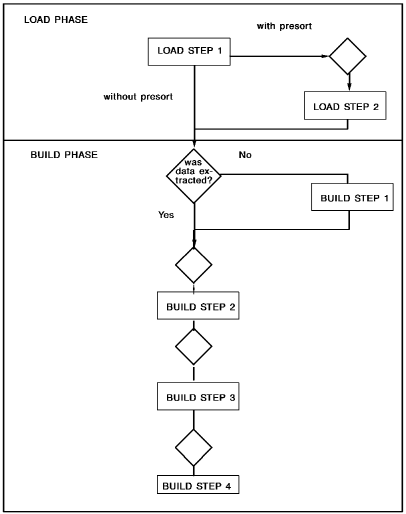
CA IDMS/DB Enforces All Constraints During the Load
CA IDMS/DB enforces all constraints during the load process. That is, it enforces:
For example, if a table allows only specified values to be stored in a column, CA IDMS/DB stores only valid values. CA IDMS/DB also assigns default values for columns for which no input values are supplied, provided the column was defined to allow null or default values.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|