

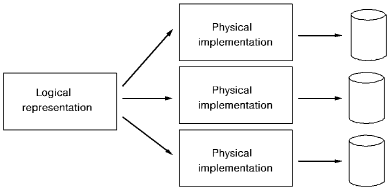
A physical database is a collection of data that resides in operating system files. CA IDMS/DB uses information provided at runtime to determine how to map the logical representation of the database to one of perhaps many physical implementations of the database.
Physical Database Represented as Segments
The definition of a physical database is represented as a segment. A segment defines the areas (that is, logical files) and physical files that contain the data in the database. For CA IDMS/DB to access the segment at runtime, the segment must be added to the definition of a DMCL.
What is a DMCL?
A DMCL is a collection of segment definitions that can be accessed in a single execution of CA IDMS/DB. A DMCL exists as a load module in a load library and is used at runtime to determine where data required by an application is physically stored.
A DMCL also performs the following tasks:
In most cases, you will need only one DMCL per configuration. For example, if you maintain separate test and production configurations, each would have its own DMCL. All applications that run under the central version use a single DMCL as specified in the system startup parameters. Applications that run in local mode can also use this DMCL.
Under local mode, you may want to use a DMCL tailored for particular applications, such as loading a database. You can specify the name of the DMCL for use in local mode in the SYSIDMS parameter file. If you do not specify a DMCL explicitly, CA IDMS/DB assumes the DMCL is named IDMSDMCL.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|