

The OBTAIN statement retrieves the named logical record and places it in the variable-storage location reserved for that logical record. The OBTAIN statement can be issued to retrieve a single logical record, or it can be issued in iterative logic to retrieve all logical records that meet criteria specified in the WHERE clause. Additionally, the OBTAIN statement can specify that the retrieved logical record is to be placed into an alternative variable storage location.
►►─── OBTAIN ─┬──────────┬─ RECORD (logical-record-name) ─────────────────────► ├─ FIRST ──┤ └─ NEXT ◄ ─┘ ►─┬──────────────────────────────────────┬─┬──────────────────────────────┬──► └─ INTO (alt-logical-record-location) ─┘ └─ WHERE (boolean-expression) ─┘ ►─┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────┬─ ; ─────────────────►◄ └─ ON LR_STATUS (path-status) imperative-statement ─┘
Retrieves the first occurrence of the logical record. OBTAIN FIRST is typically used to retrieve the first in a series of logical-record occurrences following the iterative retrieval of a different series of logical-record occurrences.
Retrieves a (subsequent) occurrence of the named logical record, in the order specified by the DBA in the path. OBTAIN NEXT is typically issued in iterative logic to retrieve a series of logical-record occurrences (possibly including the first).
When LRF receives repeated OBTAIN NEXT commands, it replaces field values in program variable storage with new values obtained through repeated access to the appropriate database records, thereby supplying the program with new occurrences of the desired logical record.
If an OBTAIN FIRST statement is followed by an OBTAIN NEXT statement to retrieve a series of occurrences of the same logical record, the OBTAIN statements must direct LRF to the same path. For this reason, you must ensure that the selection criteria specified in the WHERE clause that accompanies the OBTAIN FIRST and OBTAIN NEXT statements describe the same attributes of the desired logical record.
If the program issues an OBTAIN NEXT statement without issuing an OBTAIN FIRST, or if the last path status returned for the path was LR_NOT_FOUND, LRF interprets the OBTAIN NEXT as OBTAIN FIRST. After LR_ERROR or a DBA-defined path status, LRF does not interpret OBTAIN NEXT as OBTAIN FIRST.
Defines the named logical record occurrence, as specified in program variable storage. Logical-record-name must specify a logical record defined in the subschema.
Specifies an alternative location in variable storage into which LRF will place the retrieved logical record. Any subsequent MODIFY, STORE, or ERASE statements for a logical record placed in alt-logical-record-location should name that area as the one from which LRF will obtain the data to be used to update the logical record.
Specifies the selection criteria to be applied to the named logical record. For details on coding this clause, see Logical-Record Clauses (WHERE and ON) at the end of this chapter.
Specifies the action to be taken if path-status is returned to the LR_STATUS field in the LRC block. Path-status must be a 1- to 16-character alphanumeric value. For details on coding this clause, see Logical-Record Clauses (WHERE and ON) at the end of this chapter.
The following Example illustrates the use of the OBTAIN NEXT statement to retrieve a series of logical-record occurrences. The program issues the OBTAIN NEXT statement iteratively to retrieve the first and all subsequent occurrences of the EMP_JOB_LR logical record for all employees in the specified department.
GET_AN_ORDER: PROC OPTIONS(MAIN);
DEPT_ID_0410 = DEPT_ID_IN;
OBTAIN NEXT RECORD (EMP_JOB_LR)
WHERE (DEPT_ID_0410 = DEPT_ID_0410 OF LR);
IF LR_STATUS = 'LR_ERROR' THEN
CALL ERROR_PROCESSING;
IF LR_STATUS = 'LR_NOT_FOUND' THEN
CALL END_PROCESSING;
.
.
.
GO TO GET_AN_ORDER;
END GET_AN_ORDER;
The following figure illustrates the information retrieved by each OBTAIN NEXT statement.
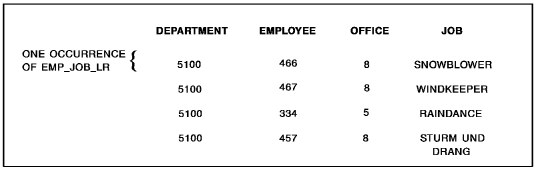
The EMP_JOB_LR logical record consists of DEPARTMENT, OFFICE, EMPLOYEE, and JOB information.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|