

Data Manipulation Language Statements › STORE RECORD
STORE RECORD
The STORE RECORD statement performs the following functions:
- Acquires space and a database key for a new record occurrence in the database
- Transfers the value of the appropriate elements from program variable storage to the specified record occurrence in the database
- Connects the new record occurrence to all sets for which it is defined as an automatic member
Steps Before Executing STORE RECORD
Before executing the STORE RECORD statement, satisfy the following conditions:
- Ready all areas affected either implicitly or explicitly in one of the update usage modes (see READY, earlier in this chapter).
- Make sure the program initializes all control elements (that is, CALC and sorted set control fields).
- If the record being stored has a location mode of DIRECT, initialize the contents of DIRECT_DBKEY (positions 197-200 of the IDMS communications block, as described in Communications Blocks and Error Detection) with a suggested db-key value or a null db-key value of -1.
- If the record is to be stored in a native VSAM relative-record data set (RRDS), initialize the contents of DIRECT_DBKEY with the relative-record number that represents the location within the data set where the record is to be stored.
- Include in the subschema all sets in which the named record is defined as an automatic member, and the owner record of each of those sets. Sets for which the named record is defined as a manual member need not be defined in the subschema since the STORE RECORD statement does not access those sets. (An automatic member is connected automatically to the selected set occurrence when the record is stored; a manual member is not connected automatically to the selected set occurrence.)
- If the record being stored has a location mode of VIA, establish currency for that VIA set, regardless of whether the record being stored is an automatic or manual member of that set. Current of the VIA set provides the suggested page for the record being stored.
- Establish currency for all set occurrences in which the stored record will participate as an automatic member. Depending on set order, the STORE RECORD statement uses currency as follows:
- If the named record is defined as a member of a set that is ordered FIRST or LAST, the record that is current of set establishes the set occurrence to which the new record will be connected.
- If the named record is defined as a member of a set that is ordered NEXT or PRIOR, the record that is current of set establishes the set occurrence into which the new record will be connected and determines its position within the set.
- If the named record is defined as a member of a sorted set, the record that is current of set establishes the set occurrence into which the new record will be connected. The DBMS compares the sort key of the new record with the sort key of the current record of set to determine if the new record can be inserted into the set by movement in the next direction. If it can, the current of set remains positioned at the record that is current of set and the new record is inserted. If it cannot, the DBMS finds the owner of the current of set (not necessarily the current occurrence of the owner record type) and moves as far forward in the next direction as is necessary to determine the logical insertion point for the new record.
Location Modes
A record is stored in the database based on the location mode specified in the schema definition of the record. The location modes are as follows:
- CALC—The record being stored is placed on or near a page calculated by IDMS DB from a control element (the CALC key) in the record.
- VIA—The record being stored is placed either as close as possible to the current of set (if current of set and member record occurrences share a common page range) or in the same relative position in the member record's page range as the current of set is in its associated page range (if current of set and member record occurrences do not share a common page range).
- DIRECT—The record being stored is placed on or near a user-specified page as determined by the value in the DIRECT_DBKEY field of the IDMS DB communications block. If DIRECT_DBKEY contains a valid db-key for the record being stored, the DBMS assigns a db-key on the same page if space is available to the new record occurrence. Otherwise, it assigns the next available db-key, subject to the page-range limits of the record being stored. If DIRECT_DBKEY contains a value of -1, the first db-key available in the page range in which the record is to be stored is assigned to the record. In any case, the db-key of the stored record occurrence is returned to DBKEY (positions 13-16 in the CA IDMS/DB communications block). The contents of DIRECT_DBKEY remain unchanged.
Currency
Following successful execution of a STORE RECORD statement, the stored record becomes current of run unit, its record type, its area, and all sets in which it participates as owner or automatic member.
Syntax
►►─── STORE RECORD (record-name);─────────────────────────────────────────────►◄
Parameter
- record-name
-
Defines the named record occurrence, as specified in program variable storage. Record-name must specify a record type included in the subschema.
The ordering rules for each set govern the insertion point of the specified record in the set.
Example
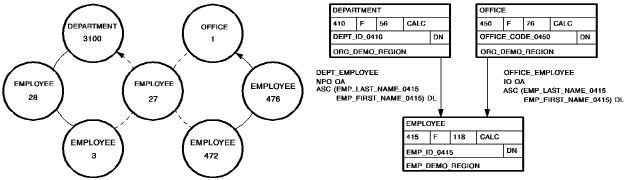
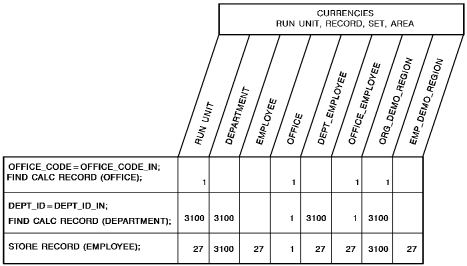
The following figure illustrates the steps necessary to add a new EMPLOYEE record to the database. Since EMPLOYEE is defined as an automatic member of both the DEPT_EMPLOYEE and OFFICE_EMPLOYEE sets, currency must be established in each of those sets before issuing the STORE RECORD.
The first two DML statements establish OFFICE 1 and DEPARTMENT as current of the OFFICE_EMPLOYEE and DEPT_EMPLOYEE sets, respectively. When EMPLOYEE 27 is stored, it is connected automatically to each set.
Status Codes
Upon completion of the STORE RECORD function, the ERROR_STATUS field in the IDMS DB communications block indicates the outcome of the operation:
- 0000
-
The request has been serviced successfully.
- 1201
-
The area in which the named record is to be stored has not been readied.
- 1202
-
The suggested DIRECT_DBKEY value is not within the page range for the named record.
- 1205
-
Storage of the record would violate a duplicates-not-allowed option for a CALC record, a sorted set, or an index set.
- 1208
-
The named record is not in the subschema. The program has probably invoked the wrong subschema.
- 1209
-
The named record's area has not been readied in one of the update usage modes.
- 1210
-
The subschema specifies an access restriction that prohibits storage of the named record.
- 1211
-
The record cannot be stored in the area because of insufficient space.
- 1212
-
The record cannot be stored because no db-key is available. This is a system internal error.
- 1218
-
The record has not been bound.
- 1221
-
An area other than the area of the named record occurrence has been readied with an incorrect usage mode.
- 1225
-
A set occurrence has not been established for each set in which the named record is to be stored.
- 1233
-
At least one set in which the record participates as an automatic member has not been included in the subschema.
- 1253
-
The subschema definition of an indexed set does not match the indexed set's physical structure in the database.
- 1254
-
Either the prefix length of an SR51 record is less than zero or the data length is less than or equal to zero.
- 1255
-
An invalid length has been defined for a variable length record.
- 1260
-
A record occurrence that was encountered in the process of connecting automatic sets is inconsistent with the set named in the ERROR_SET field of the CA IDMS/DB communications block; probable causes include a broken chain or improper database description.
- 1261
-
The record cannot be stored because of broken chains in the database.
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|



