

You can code INCLUDE IDMS statements in your application program to copy source code into the program. The data dictionary contains one or more items of source code that correspond to each INCLUDE IDMS statement parameter. Accordingly, your choice of Parameters determines the items of code copied from the data dictionary into your program. The Syntax rules for INCLUDE IDMS (shown below) describe the INCLUDE IDMS statement Parameters with their associated items of source code.
The source code that you copy into your program depends on the usage mode defined in the program's subschema. The subschema usage modes are DML, LR, and MIXED. These usage modes determine your program's source code requirements; thus, they determine whether the program can access database records only, logical records only, or both database records and logical records. Do not code INCLUDE IDMS statements to copy items that conflict with your program's subschema usage mode. For example, do not code SUBSCHEMA_LR_CTRL if your program's subschema usage mode is DML.
The following table describes subschema usage modes and the source code each requires.
|
Subschema usage mode |
Description and required source code |
|---|---|
|
DML |
Allows a program to access database records only. DML requires the following source code items:
|
|
LR |
Allows a program to access logical records only. LR requires the following source code items:
|
|
MIXED |
Allows a program to access both database records and logical records. MIXED requires the following source code items:
Usage of MIXED mode is not recommended for the following reasons:
|
►►─┬────────────────┬─ INCLUDE IDMS ──────────────────────────────────────────► └─ level-number ─┘ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ ►─┬─ (─▼─ SUBSCHEMA_DML_LR_DESCRIPTION ─┬──┬─────────────┬────────┬┴─) ─┬ ; ─►◄ │ ├─ SUBSCHEMA_DESCRIPTION ───────┤ └─ attribute ─┘ │ │ │ ├─ SUBSCHEMA_CTRL ──────────────┤ │ │ │ ├─ SUBSCHEMA_RECORDS ───────────┘ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─ record-name ──┬──────────────────┬─┬─────────────┬─────┤ │ │ │ └─ version-number ─┘ └─ attribute ─┘ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─ TRANSACTION_STATISTICS ────────────────────────────────┤ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─ SUBSCHEMA_LR_DESCRIPTION ────┬─────┬─────────────┬─────┤ │ │ ├─ SUBSCHEMA_LR_CONTROL ────────┤ └─ attribute ─┘ │ │ │ ├─ SUBSCHEMA_LR_RECORDS ────────┘ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─ LR (logical-record-name) ──┬─────────────┬─────────────┤ │ │ │ └─ attribute ─┘ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─ MAPS ────────────────────────┬─────┬─────────────┬─────┘ │ │ ├─ MAP map-name ────────────────┤ └─ attribute ─┘ │ │ ├─ MAP_CONTROLS ────────────────┤ │ │ ├─ MAP_CONTROL map-name ────────┤ │ │ └─ MAP_RECORDS ─────────────────┘ │ │ │ └── (SUBSCHEMA_LR_CTRL) ─┬───────────────────────┬──┬─────────────┬───┘ └─ SIZE lrc-block-size ─┘ └─ attribute ─┘
Instructs the DML precompiler to copy source code into your program at the INCLUDE IDMS statement's location.
The optional level-number clause instructs the DML precompiler to copy descriptions into your program at a different level than the level specified in the data dictionary. Level-number must be an integer in the range 01 through 99. If your program specifies level-number, the DML precompiler copies the first level of code to the level specified by level-number and adjusts all other levels accordingly. If your program does not specify level-number, the descriptions copied by the DML precompiler have the same level numbers as originally specified in the dictionary.
Using the level-number clause can cause unpredictable results if record fields are defined with a SYNCHRONIZED clause. Such fields may contain slack bytes, inserted to ensure correct alignment. Because CA IDMS/DB and CA IDMS/DC do not regard slack bytes as functional, fields that contain such bytes may be misrepresented. Therefore, you should ensure that all fields and records are structured properly.
Copies all components required to access both database and logical records:
You specify SUBSCHEMA_DML_LR_DESCRIPTION only if the subschema usage mode is MIXED. Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_DML_LR_DESCRIPTION if the usage mode is DML or LR.
Copies all components required to access database records:
Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_DESCRIPTION if the subschema usage mode is LR.
Copies the IDMS DB communications block data description. If the operating mode is IDMS_DC or DC_BATCH, SUBSCHEMA_CTRL copies the IDMS DC communications block.
Copies the descriptions of all records contained in the subschema. The DML precompiler may copy into your program PL/I synonyms defined for the subschema records in the data dictionary, according to the rules of synonym usage. Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_RECORDS if the subschema usage mode is LR.
Note: When copying a schema-owned record, the DML precompiler adds up to 7 bytes, if necessary, to make the record length divisible by 8 for doubleword alignment.
Copies the description of a record defined in the dictionary. Do not specify record if the subschema's usage mode is LR.
Specifies the name of the record to be copied. It can be the primary name of a record stored in the data dictionary, or a synonym.
Schema-owned records cannot be copied into non CA IDMS programs. These are programs that neither use a subschema nor access the database. However, a synonym defined for a schema-owned record can be copied into a non CA IDMS program. You use the VERSION clause to identify the synonym.
If the DMLP processor cannot find a record named record-name in the dictionary, it searches for a module by that name. The module, which may have been stored using the DDDL compiler, presumably contains a definition of records not included in the subschema. If an operating mode is associated with the named record or module in the data dictionary, it must agree with the mode in effect for your program. (See "DECLARE SUBSCHEMA", earlier in this chapter.)
Note: For more information about associating operating modes with records, see the CA IDMS IDD DDDL Reference Guide.
Optionally qualifies IDD records, but not schema-owned records, with a version number. Version-number must be an integer in the range 1 through 9999. Version-number defaults to the highest version number of the record defined in the data dictionary for the language and operating mode under which the program compiles.
Optionally allows you to instruct the DML precompiler to include PL/I attributes in the PL/I DECLARE statement. The DML precompiler generates the PL/I DECLARE statement for the record that you specify in record-name.
Copies the definition of the transaction statistics block (TSB) with a length of 560 bytes. This block can be used in the ACCEPT TRANSACTION STATISTICS or END TRANSACTION STATISTICS DML statements.
Copies all components required to access logical records:
Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_LR_DESCRIPTION if the subschema's usage mode is DML.
Copies the SUBSCHEMA_CTRL and SUBSCHEMA_LR_CTRL components. Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_LR_CONTROL if the subschema usage mode is DML.
Copies the descriptions of all logical records defined in the subschema. All participating database records become 02-level group fields. This allows your program to reference the portion of a logical record corresponding to a database record as a group field. Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_LR_RECORDS if the subschema usage mode is DML.
Note: When copying a schema-owned record, the DML precompiler adds up to 7 bytes, if necessary, to make the record length divisible by 8 for doubleword alignment.
Copies the description of an individual logical record contained in the subschema: do not include LR if the subschema usage mode is DML.
Names the logical record.
Optionally allows you to instruct the DML precompiler to include PL/I attributes in the PL/I DECLARE statement. The DML precompiler generates the PL/I DECLARE statement for the logical record that you specify in logical-record-name.
Copies the map request block (MRB) and map records for the maps that you specify with DECLARE MAP statements.
Copies the MRB and map records associated with the named map. The map's version number defaults to the version number that you specify for this map in the DECLARE MAP statement.
Names the map.
Attribute optionally allows you to instruct the DML precompiler to include PL/I attributes in the PL/I DECLARE statement. The DML precompiler generates the PL/I DECLARE statement for the map that you specify in map-name.
Copies the MRBs for the maps that you specify in DECLARE MAP statements.
Copies the MRB for the named map. The map's version number defaults to the version number that you specify for this map in the DECLARE MAP statement.
Names a map.
Optionally allows you to instruct the DML precompiler to include PL/I attributes in the PL/I DECLARE statement. The DML precompiler generates the PL/I DECLARE statement for the map that you specify in map-name.
Copies the map records for the maps that you specify in DECLARE MAP statements.
Copies the LRC block data description.
Do not specify SUBSCHEMA_LR_CTRL if the subschema usage mode is DML.
Optionally specifies the size of that portion of the LRC block that contains information about the logical-record-request WHERE clause (PXE).
Lrc-block-size defaults to 512 bytes. If you include lrc-block-size, you should specify a size large enough to accommodate the most complex WHERE clause in the program. The default, 512, is large enough to include approximately 32 operators, operands, and literals.
Lrc-block-size must be a positive integer in the range 0 through 9999. You specify a value of 0 if none of the logical-record requests issued by the program includes a WHERE clause. You calculate lrc-block-size as follows:
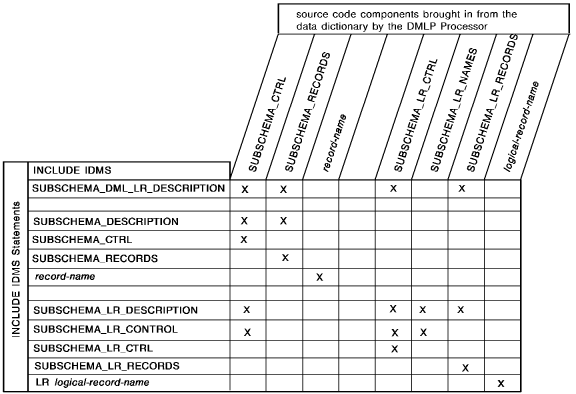
The following figure shows the code that the DML precompiler copies into program variable storage for each INCLUDE IDMS statement parameter.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|