

The @FIND/@OBTAIN WITHIN SET/AREA statement accesses records logically based on set relationships or physically based on database location. The formats of this statement allow you serial access to each record in a set or area, or selection of specific occurrences of a given record type in a set or area.
Set currency
The following rules apply to currency and the selection of member records in a set:
Note: Note 1If @OBTAIN has been specified, the contents of the owner record are not moved to program variable storage (@OBTAIN under these circumstances is treated as an @FIND).
Note: Note 2(Native VSAM users): When an end-of-set condition occurs, all currencies remain the same.
Area currency
The following rules apply to currency and the selection of records in an area:
Following successful execution of an @FIND/@OBTAIN WITHIN SET/AREA statement, the accessed record becomes the current record of run unit, its area, its record type, and all sets in which it currently participates as member or owner.
Syntax
►►─┬─ @FIND ───┬─┬─ NEXT ──┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────► └─ @OBTAIN ─┘ ├─ PRIOR ─┤ ├─ FIRST ─┤ ├─ LAST ──┤ └─ NTH ───┘ ►─┬─ ,SET=set-name ───┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────► └─ ,AREA=area-name ─┘ ►─┬────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────────► └─ ,REC=record-name ─┘ ►─┬───────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────► └─ ,OCCUR=sequence ─┘ ►─┬───────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────►◄ └─ ,KEEP= ─┬─ SHARED ──────┬┘ └─ EXCLUSIVE ───┘
Parameters
Accesses a record based on its location in a set or area.
Accesses the next record in the specified set or area relative to the current record of the set or area.
Accesses the prior record in the specified set or area relative to the current record of the set or area. The specified set must have prior pointers.
Accesses the first record in the specified set or area.
Accesses the last record in the specified set or area. The specified set must have prior pointers.
Accesses the nth record in the specified set or area. NTH requires the use of the OCCUR parameter (see below) to specify which record is to be accessed.
Note: Native VSAM users—FIRST, LAST, and NTH options are not allowed for a native VSAM KSDS with spanned records.
Specifies the set or area to be searched.
Specifies the name of the set that contains the record to be accessed. Set-name must identify an set included in the subschema.
Specifies the name of the area that contains the record to be accessed. Area-name must identify an area included in the subschema.
Specifies that in a set or area, only occurrences of the named record type will be accessed.
Must be defined as a member of the specified set or contained in the specified area.
Identifies the position of the record in the set (that is, the numeric occurrence that is associated with the keyword NTH).
Must specify a positive or negative number that is stored in a numerical field used by CA IDMS/DB in searching for the nth record occurrence. If sequence specifies a negative number, the specified set must have prior pointers.
Places a shared or exclusive lock on the accessed record.
Places a shared lock on the specified record.
Places an exclusive lock on the specified record.
Example
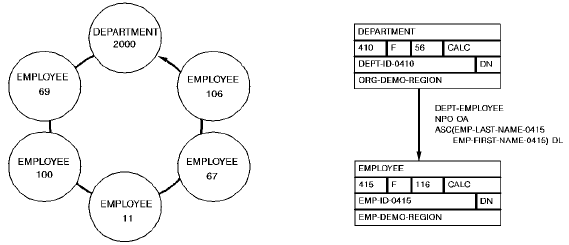
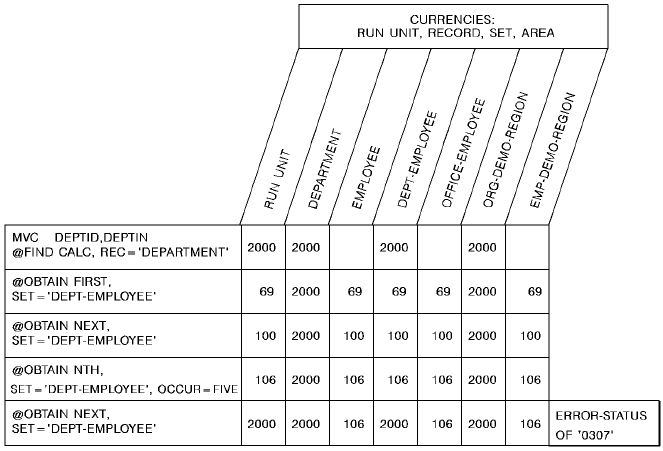
The following example illustrates the retrieval of records in an occurrence of the DEPT-EMPLOYEE set. The @FIND CALC statement establishes currency in the DEPT-EMPLOYEE set. Member EMPLOYEE records are then retrieved by a series of OBTAIN WITHIN SET statements. Note that when EMPLOYEE 106 is retrieved, the end of the set is reached and the next OBTAIN statement positions the program on the owner of the set, DEPARTMENT 2000.
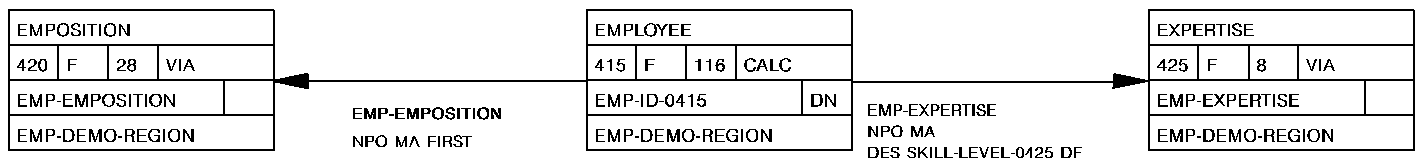
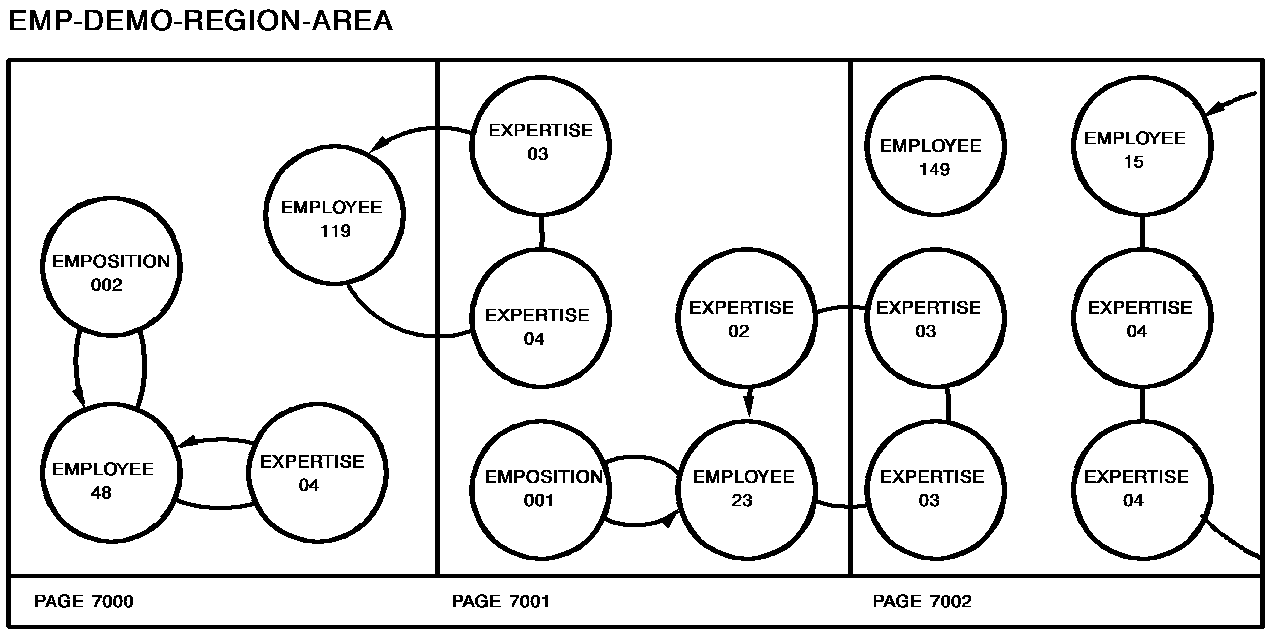
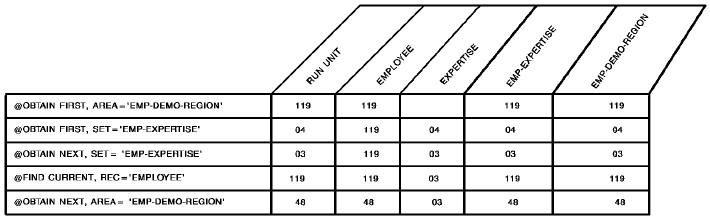
The following figure illustrates special considerations relating to the retrieval of records in an area that contains multiple record types. In this example, the user wishes to sweep the EMP-DEMO-REGION area, retrieving sequentially each EMPLOYEE record and all records in the associated EMP-EXPERTISE set. The first command retrieves EMPLOYEE 119. Subsequent @OBTAIN WITHIN SET statements retrieve the associated EXPERTISE records and establish currency on EXPERTISE 03. The @FIND DBKEY statement is used to reestablish the proper position before retrieving EMPLOYEE 48. Note that if @FIND DBKEY for the employee record is not specified, an attempt to retrieve the next EMPLOYEE record in the area would return EMPLOYEE 23.
Status codes
After completion of the @FIND/@OBTAIN WITHIN SET/AREA function, the ERRSTAT field in the IDMS communications block indicates the outcome of the operation. The following is a list of the acceptable status codes for this function and their corresponding meaning:
This request has been serviced successfully.
The area in which the named record participates has not been readied.
A sequence number of zero or a variable field that contains a value of zero was specified for the named record.
Currency has not been established for the named record, set, or area.
The end of the set or area has been reached, or the set is empty.
Either the named record or the named set is not in the subschema, or the named record is not defined as a member of the named set. The program has probably invoked the wrong subschema, or has misspelled the record or set name.
The subschema specifies an access restriction that prohibits retrieval of the named record.
The area name specified has not been included in the subschema invoked, the record name specified has not been defined in the named area, or the area name has been misspelled.
The record cannot be found.
A record occurrence has been encountered whose record type is not a member or owner of the set as it is defined in the subschema.
The record cannot be stored because of broken chains in the database.
A database file will not open properly.
When the KEEP parameter is specified as part of the @FIND/@OBTAIN statement a major code of 06 will be returned if an error occurs during the KEEP processing (see @KEEP in this chapter). The major code of 03 states that an error has occurred in the @FIND/@OBTAIN processing.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|