

Functions of @STORE
The @STORE statement performs the following functions:
Location Modes
A record is stored in the database according to the location mode specified in the schema definition of the record. The location modes are as follows:
In any case, the db-key of the stored record occurrence is returned to DBKEY (positions 13-16 in the IDMS communications block). The contents of DIRDBKEY remain unchanged.
Before Executing @STORE
Before execution of the @STORE statement, the following conditions must be met:
Currency
Currency must be established for all set occurrences in which the stored record will participate as an automatic member. The @STORE statement uses currency depending on how the set is ordered:
Following successful execution of an @STORE statement, the stored record becomes current of run unit, its record type, its area, and all sets in which it participates as owner or automatic member.
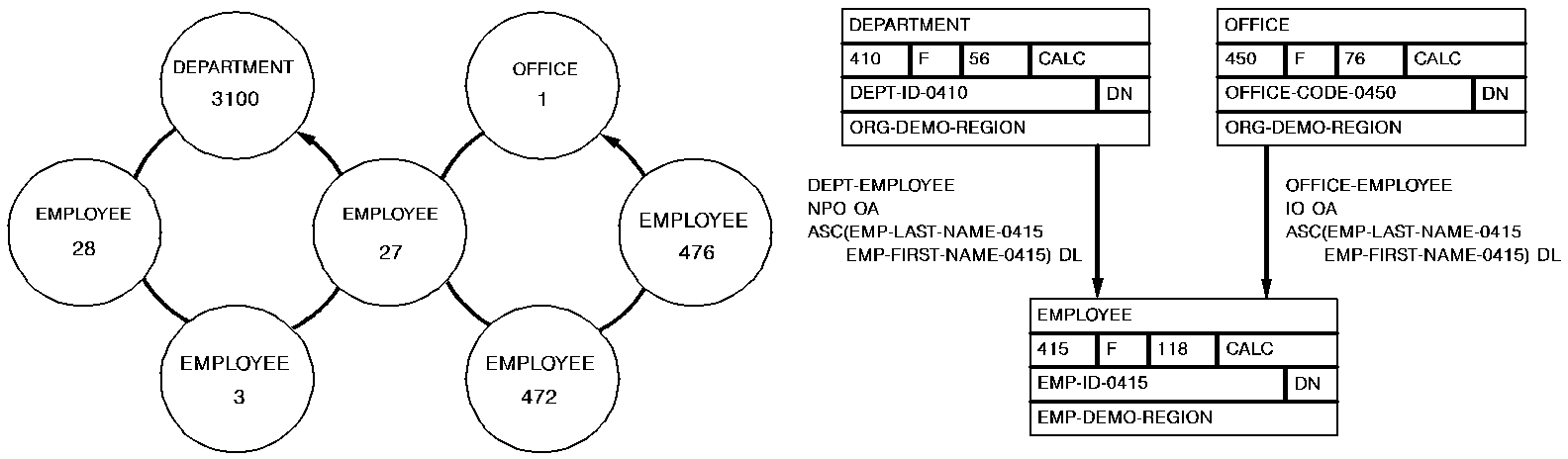
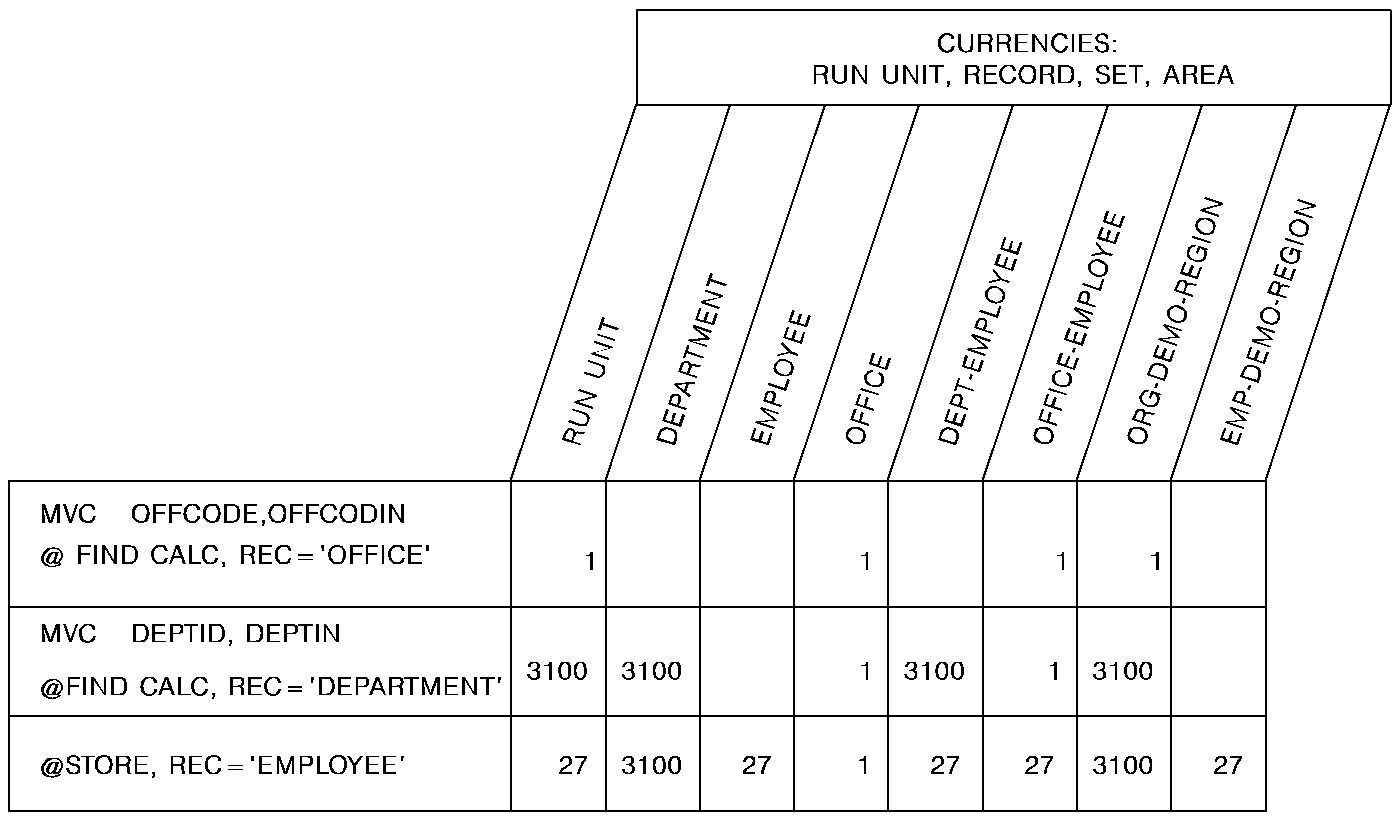
The following figure illustrates the currency issues involved in adding a new EMPLOYEE record to the database.
Since EMPLOYEE is defined as an automatic member of both the DEPT-EMPLOYEE and OFFICE-EMPLOYEE sets, currency must be established in each of those sets before issuing the @STORE statement. The first two DML commands establish DEPARTMENT-3100 and OFFICE-1 as current of the DEPT-EMPLOYEE and OFFICE-EMPLOYEE sets, respectively. When EMPLOYEE-27 is stored, it is connected automatically to each set.
Syntax
►►─── @STORE REC=record-name ─────────────────────────────────────────────────►◄
Parameters
Specifies the record occurrence to be moved from variable storage to the database. The @STORE statement connects the requested record to an occurrence of each set for which it is defined as an automatic member, and establishes it as the owner of a set. The @STORE statement also establishes the named record as the owner of a set occurrence for each set for which it is defined as an owner. The ordering rules for each set govern the insertion point of the named record in the set. Record-name must specify a record type included in the subschema.
Example
The @STORE statement shown below performs the following:
@STORE REC=EMPLOYEE
Status Codes
After the completion of the @STORE function, the ERRSTAT field in the IDMS communications block indicates the outcome of the operation. The following is a list of the acceptable status codes for this function and their corresponding meaning:
The area in which the named record is to be stored has not been readied.
The suggested DIRDBKEY value is not in the page range for the named record.
Storage of the record would violate a duplicates-not-allowed option for a CALC record, a sorted set, or an index set.
The named record is not in the subschema. The program has probably invoked the wrong subschema, or the record name has been misspelled.
The named record's area has not been readied in one of the three update usage modes.
The subschema specifies an access restriction that prohibits storage of the named record.
The record cannot be stored in the area because of insufficient space.
The record cannot be stored because no db-key is available. This is a system internal error.
The record has not been bound.
An area other than the area of the named record occurrence has been readied with an incorrect usage mode.
A set occurrence has not been established for each set in which the named record is to be stored.
All sets in which the record participates as an automatic member have not been included in the subschema.
The subschema definition of an indexed set does not match the indexed set's physical structure in the database.
Either the prefix length of an SR51 record is less than zero or the data length is less than or equal to zero.
An invalid length has been defined for a variable-length record.
A record occurrence encountered in the process of connecting automatic sets is inconsistent with the set named in the ERRORSET field of the IDMS communications block; probable causes include a broken chain or an improper database description.
The record cannot be stored because of broken chains in the database.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|