

The logical-record request control (LRC) block passes information between the application program and LRF. It is used in conjunction with the IDMS communications block to pass information to LRF about a logical-record request and to return path status information about the processing of the request to the program.
To receive information about a logical-record request, the application program must define the LRC block in variable storage. You must either copy the LRC block from the dictionary into the program's variable storage by using the @COPY IDMS statement or generate the LRC block by using the @SSLRCTL statement. The following example illustrates the @COPY IDMS statement before and after expansion by the DML precompiler:
@COPY IDMS,SUBSCHEMA-LR-CTRL (before DML expansion)
* @COPY IDMS,SUBSCHEMA-LR-CTRL (after DML expansion)
DS 0D
SSLRCTL DS 0CL576
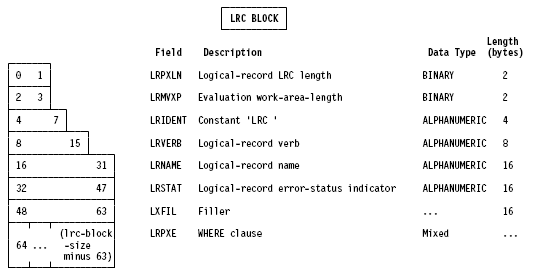
LRPXLN DS HL2
LRMVXP DS HL2
LRIDENT DC CL4'LRC '
LRVERB DC CL8' '
LRNAME DC CL16' '
LRSTAT DC CL16' '
LRFILL DC CL16' '
LRPXE DS 512CL1
The same expansion would result by using the @SSLRCTL statement in your application program instead of the @COPY IDMS,SUBSCHEMA-LR-CTRL statement. The @SSLRCTL statement is a macro that generates the variable storage definitions of the LRC block instead of copying the block from the dictionary. For more information about the differences between these statements, see DML Precompiler-Directive Statements .
When a program issues a logical-record request, the LRC block stores the DML verb used by the program, the name of the logical-record, and the selection criteria of the request. LRF uses this information to select the appropriate path to handle the request.
After LRF has processed a request, it returns path status information in the LRC block. After issuing the path status, LRF returns an error-status code in the ERRSTAT field of the IDMS communications block. You can use this information to evaluate the result of the request and to determine further processing based on that result. The following figure shows the layout of the LRC block; each field is described separately following the figure.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|