

A RECORD statement names a CA IDMS/DB record and optionally specifies either the type of CA IDMS/DB ERASE command issued or that a DISCONNECT command was issued. The CA IDMS/DB ERASE or DISCONNECT command is issued in response to a DL/I DLET call for the segment corresponding to the named record.
To determine the RECORD statements required for an IPSB:
Syntax
►►─── RECORD SECTION ── . ───────────────────────────────────────────────────► ►─── RECORD name is idms-record-name ───────────────────────────────────────► ►─── LENGTH is ─┬─ dl1-segment-length ────────────────────────────┬─────────► └─ dl1-max-segment-length dl1-min-segment-length ─┘ ►─┬───────────────────────────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────►◄ └─ DELete by ──┬── ERASE ALL ◄──────┬─── . ─────┘ ├── ERASE PERManent ─┤ ├── ERASE SELective ─┤ └── DISConnect ──────┘
Parameters
Identifies the CA IDMS/DB record to be accessed by the CA IDMS DLI Transparency run-time interface.
Idms-record-name must be a 1- to 16-character name that corresponds to a DL/I segment and must be defined in the subschema named in the IPSB SECTION.
Specifies the length of the DL/I segment to which the idms-record-name corresponds.
Specifies the length of the DL/I segment if it is a fixed-length segment.
Specifies the maximum and minimum lengths of the DL/I segment if it is a variable-length segment. See "Determining values for variable length segments" under "Examples" later in this chapter.
Specifies the CA IDMS/DB DML command that the interface will issue in response to a DL/I DLET call for the segment corresponding to the named record.
Specifies that the named record and all mandatory and optional member record occurrences it owns are to be erased.
All members that are owners of any set occurrences are treated as if they were the object of an ERASE ALL statement.
ERASE ALL is the default.
Specifies that the named record and all mandatory member record occurrences it owns are to be erased from the database. Optional member record occurrences are disconnected.
All erased mandatory members that are owners of set occurrences are treated as if they were the object of an ERASE PERMANENT statement.
Note: For more information about CA IDMS/DBset membership options, see the CA IDMS Database Administration Guide
Specifies that the named record and all mandatory member record occurrences it owns are to be erased from the database. Optional member record occurrences are erased only if they do not currently participate as members in other set occurrences.
All erased members that are owners of set occurrences are treated as if they were the object of an ERASE SELECTIVE statement.
Specifies that the membership of the named record is cancelled from all sets in which it currently participates as an optional member. The record, however, remains in the database.
Usage
Determining the Value for a Fixed Length Segment
To locate the dl1-segment-length, find the SEGM statement defining the segment that corresponds to the named record. Use the entry in the SEGM statement's BYTES clause for dl1-segment-length.
Note that if the DL/I segment is a logical child segment, the length of the physical and/or logical parent concatenated key may be required along with the BYTES clause entry when determining the value of dl1-segment-length.
Determining Values for Variable Length Segments
To locate dl1-max-segment-length and dl1-min-segment-length values, find the SEGM statement defining the segment that corresponds to the named record. Use the first entry in the SEGM statement's BYTES clause for dl1-max-segment-length; use the second entry in the SEGM statement's BYTES clause for dl1-min-segment-length.
Note that if the DL/I segment is a logical child segment, the length of the physical and/or logical parent concatenated key may be required along with the BYTES clause entries when determining the value for dl1-max-segment-length and dl1-min-segment-length.
Calculating the Length of a Concatenated Key
The length of a concatenated key equals the sum of the lengths of the sequence field, from the sequence field of the named key through the root segment's sequence field.
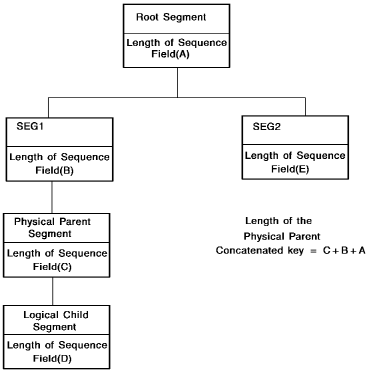
Figure 36. Finding the length of a concatenated key
Determining Record Length for Logical Child Equivalent
The examples below show how you can determine the record length for the logical child equivalent.
Refer to "LOGICAL PARENT FIELD Statement" later in this section for details on determining whether the physical parent concatenated key and the logical parent concatenated key are stored virtually or physically.
Example 1
Assume the LPCK is stored virtually and the PPCK is stored physically.

For fixed-length segments:
dl/i-segment-length = (BYTES entry - LPCK-length) + PPCK-length
For variable-length segments:
dl/1-max-segment-length = (First BYTES entry - LPCK-length) + PPCK-length dl/1-min-segment-length = (Second BYTES entry - LPCK-length) + PPCK-length
Example 2

Assume both the PPCK and the LPCK are stored virtually.
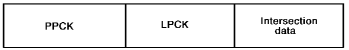
Find the LPCK's length. Subtract this key length from the entry(ies) in the logical child's BYTES clause:
For fixed length segments:
dl/i-segment-length = BYTES entry - LPCK-length
For variable length segments:
dl/1-max-segment-length = First BYTES entry - LPCK-length
dl/1-min-segment-length = Second BYTES entry - LPCK-length
Example 3
Assume that the logical parent concatenated key (LPCK) is stored physically and the physical parent concatenated key (PPCK) is stored virtually.

Use the BYTES parameter value(s) in the logical child's SEGM statement as the value(s) for the LENGTH parameter:
For fixed length segments:
dl/i-segment-length = BYTES entry in logical child's SEGM statement
For variable length segments:
dl/1-max-segment-length = First BYTES entry in logical child's SEGM statement
dl/1-min-segment-length = Second BYTES entry in logical child's SEGM statement
Example 4
Assume both the LPCK and the PPCK are stored physically.
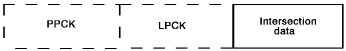
Find the PPCK's length. Add this key length to the entry(ies) in the logical child's BYTES clause:
For fixed length segments:
dl/i-segment-length = PPCK-length + BYTES entry in logical child's SEGM statement
For variable length segments:
dl/1-max-segment-length = PPCK-length + first BYTES entry in logical child's SEGM statement
dl/1-min-segment-length = PPCK-length + second BYTES entry in logical child's SEGM statement
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|