

DBD Definition for a Logical Database
The sample below shows the DBD source statements for a logical database. The DBD definitions for the underlying physical databases are those shown in Figure 9. In the logical DBD shown below, LSEGB is the concatenated segment that combines the SEG6 and SEG1 segments from PHYSDB1 and PHYSDB2, respectively.
DBD NAME=LOGDB,ACCESS=LOGICAL
DATASET LOGICAL
SEGM NAME=LSEGA,SOURCE=((SEG5,PHYSDB2))
SEGM NAME=LSEGB,PARENT=LSEGA,
SOURCE=((SEG6,DATA,PHYSDB2),(SEG1,DATA,PHYSDB1))
SEGM NAME=SEG3,PARENT=(LSEGB,((SEG3,PHYSDB1)))
SEGM NAME=SEG4,PARENT=LSEGB,SOURCE=((SEG4,PHYSDB1))
SEGM NAME=SEG7,SOURCE=((SEG7,PHYSDB2)),PARENT=LSEGB
SEGM NAME=SEG8,SOURCE=((SEG8,PHYSDB2)),PARENT=LSEGB
DBDGEN
FINISH
END
Logical Database Structure
The illustration below shows the logical database produced by the logical DBD definition in the source statements shown above. Compare the resulting logical structure with the hierarchical structures for the underlying physical databases.
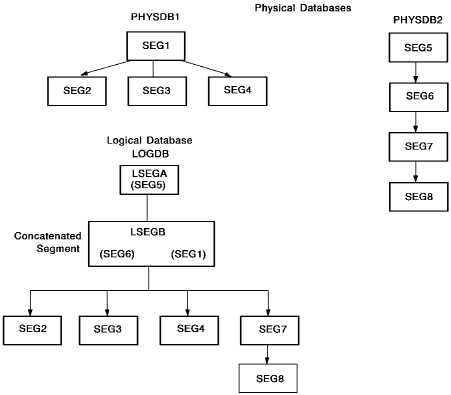
Figure 17. Logical database structure
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|