

Each of the four access methods allowed for physical DBDs requires a different implementation in CA IDMS/DB. The HSAM, HISAM, HDAM, and HIDAM access methods are discussed below.
HSAM
CA IDMS DLI Transparency does not implement HSAM databases directly. However, the indirect implementation is transparent to any DL/I application using an HSAM database. The CA IDMS DLI Transparency implementation depends on whether the HSAM database is sequenced or unsequenced:
HISAM
CA IDMS DLI Transparency relates the root segment in the HISAM database to the member record type in a system-owned indexed set. The member record has a location mode of DIRECT; its symbolic key corresponds to the root segment's sequence field. If it is necessary to keep the member record (the root segment equivalent) in physical sequential order, ascending or descending order is defined for its symbolic key.
Note: For more information about indexed sets, see the CA IDMS Database Administration Guide.
Sample HISAM Database and CA IDMS/DB Sets
The diagram below, shows a sample HISAM database and the CA IDMS/DB sets used to implement it.
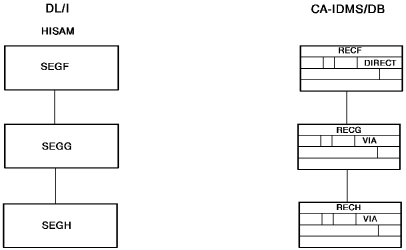
Figure 22. Sample HISAM database and corresponding CA IDMS/DB sets
HDAM
In CA IDMS DLI Transparency, the root segment in an HDAM database corresponds to an owner record type with a location mode of CALC. The root segment's sequence field is defined as the CALC key.
Sample HDAM Hierarchy and CA IDMS/DB Sets
The diagram below shows a sample HDAM hierarchy and the corresponding CA IDMS/DB set structures.
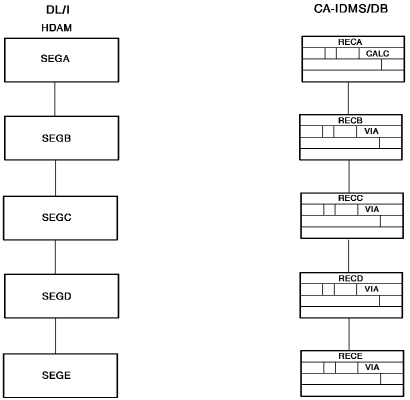
Figure 23. Sample HDAM hierarchy and corresponding CA IDMS/DB sets
HIDAM
As with an HDAM database, the HIDAM root segment is defined as an owner record with a location mode of CALC. The root segment's sequence field becomes the CALC key.
In a HIDAM database, the root segment is also the source and target segment for the associated index database. To account for the index pointer segment, a member record type is defined with a location mode of VIA within an indexed set owned by the CALC owner record type. The index record contains a single element to match the root segment's sequence field (CALC key in the owner record type). The index record also contains any data fields defined in the index. During processing, CA IDMS/DB maintains matching occurrences between the index (member) record and the owner of the set.
Sample HIDAM Hierarchy and CA IDMS/DB Sets
The diagram below shows a sample HIDAM hierarchy and the corresponding CA IDMS/DB set structures.
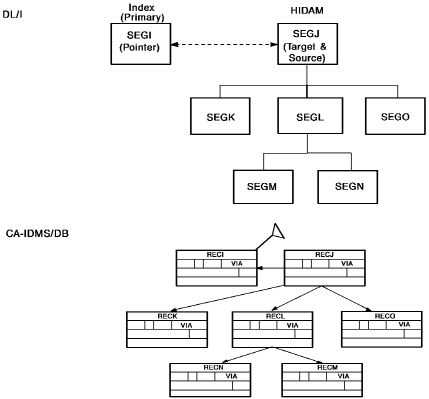
Figure 24. Sample HIDAM hierarchy and corresponding CA IDMS/DB sets
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|