

There are two types of errors in sorted sets:
1. Sorted set is out of sequence
In a set that is sorted in descending order, the sort key of the previous record in the set is greater than the sort key of the current record. In a set that is sorted in ascending order, the sort key of the previous record is less than the sort key of the current record. For example, in Figure 2.10, the DEPT-TEACHER set should be sorted in ascending order by last-name. Jane Doe is out of sequence, however; she should precede Harold Jones in the set. CA IDMS/DB Audit corrects this set so that ENGLISH points to Jane Doe, Jane Doe points to Harold Jones, and Harold Jones points to Carol Smith.
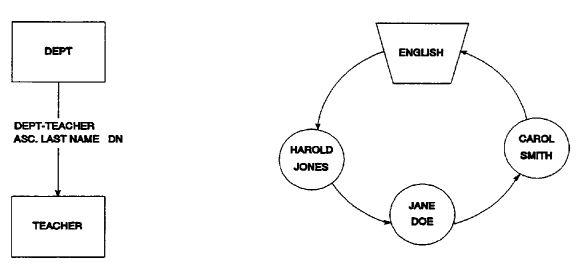
Figure 2.10: Sorted Set Out of Sequence
2. Duplicates in a sorted set when duplicates are not allowed
The sort key of the current record equals the sort key of the previous record in the set occurrence. For example, in Figure 2.11, duplicates are not allowed within the DEPT-TEACHER set. David Herman, however, is found to be in the set twice. CA IDMS/DB Audit does not fix this type of error.
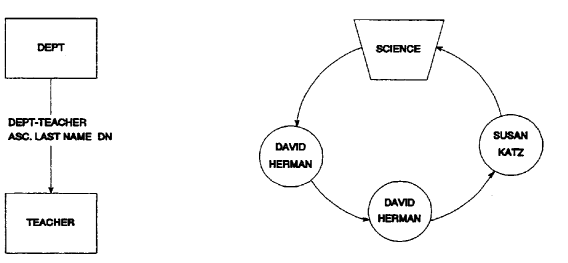
Figure 2.11: Sorted Set with Duplicates
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|