

CA Culprit in the CA IDMS/DB Environment › Database Record Access
Database Record Access
By using database records, the user can specify a path to navigate the a non-SQL defined database. The path consists of a string of one or more database records connected according to established set relationships. The following figure illustrates a non-SQL defined database structure in which the records participate in set relationships.
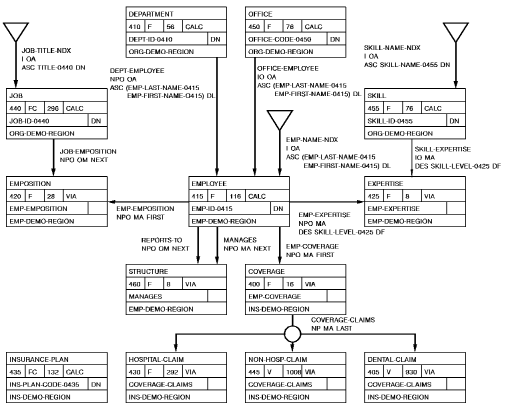
Note: CA Culprit navigates the database according to the set relationships that connect one record type to another.
CA Culprit can access records in a database by using an area sweep, that is, sequentially within an area or directly by using a CALC-key value, a db-key value, or an index-key value:
- A CALC-key value is a value of a designated field in the record, such as the employee ID field. In the figure given earlier, the EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT, OFFICE, JOB, SKILL, and INSURANCE-PLAN records can be accessed by using a CALC-key value.
- A db-key (database key) value identifies the physical address of the record in the database. Every record can be retrieved by using its db-key value.
- An index-key value is a value of a designated field in the record that has an index established on it; for example, the EMPLOYEE record is indexed according to employee last names. The SKILL and JOB records in the figure given earlier are also indexed.
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


