

Purpose
Define what action to take based on a comparison of values held by different fields.
Syntax
►►─┬─ IF boolean-expression ─┬──┬─ result-action ─┬───────────────────────────►◄ ├─ if EOF ─┬┬─ EQ ─┬┬─────┤ └─ sequence ──────┘ │ │└─ = ──┘│ │ │ └┬─ NE ─┬┘ │ │ └─ # ──┘ │ └┬─ B ────┬───────────────┘ └─ GOTO ─┘
Expansion of Boolean-expression
┌───────────────────────────┬─ AND ─┬────────────────────────────────────┐ │ └─ OR ──┘ │ ►►─▼─┬ literal ──────────────┬ test-operation ─┬┬─ NUMERIC ───────────────┬┬┴─►◄ └ field-name-expression ┘ │├─ literal ───────────────┤│ │└─ field-name-expression ─┘│ └ ( field-name-range ) ─────┘
Expansion of Result-action
►►─┬─ DROP ───────┬───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────►◄ ├─ TAKE ───────┤ ├─ RELS ───────┤ ├┬─ STOP-RUN ─┬┤ │└─ STOP ─────┘│ ├─ STOP-RPT ───┤ ├─ HEAD ───────┤ └─ USnn ───────┘
Expansion of Field-name-range
►►──┬─ literal ───────────────┬─ TO ─┬─ literal ───────────────┬─────────────►◄ └─ field-name-expression ─┘ └─ field-name-expression ─┘
Syntax Rules
Specifies a test operation. IF is a required CA Culprit reserved word that indicates a compound test operation. IF is an optional keyword for a simple test operation unless parentheses enclose the operation. For boolean-expression, see the explanation of the expanded syntax below.
Specifies a test for an end-of-file condition.
This test is valid only on a type 7 process parameter. EQ/NE indicates the type of test to be performed:
|
Test |
What it means |
|---|---|
|
Eq |
Indicates that the specified action occurs if end-of-file is reached. |
|
Ne |
Indicates that the specified action occurs if end-of-file has not been reached. |
A STOP-RUN or a STOP-RPT instruction cannot be specified as a result action on an EOF conditional operation.
When end-of-file is reached, the procedure logic is evaluated a final time, starting with the first procedure statement. Processing continues until a DROP, TAKE, or STOP-RUN instruction executes. Once one of these instructions executes, the current buffer does not reenter the type 7 procedure logic for the report.
Directs CA Culprit to perform an unconditional branch.
Indicates the action to be performed as a result of a true test condition or an unconditional branch statement.
See expanded syntax below for possible values for result-action.
The sequence number of a process parameter that receives processing control. Processing control must be passed to a process parameter of the same type; For example, from one type 7 parameter to another or from one type 8 parameter to another.
The process statement that receives processing control must have a sequence number coded in columns 5 through 7.
Expansion of Boolean-expression
Specifies the value of the left operand.
Syntax and syntax rules for coding field-name-expression appear in User-Defined Variables. The left and right operands of a test operation must contain data that is compatible for comparison. The following table presents combinations of data types that can be compared in a test operation.
Alphanumeric data and numeric data are compared as follows:
Valid Left and Right Operand Data Types and Associated Test Operations
|
Left Operand |
Valid Test Operators* |
Right Operand |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
EQ/NE |
GT/LT/GE/LE |
||
|
Numeric literal |
l |
l |
Numeric literal |
|
|
l |
l |
Numeric input or work field |
|
Numeric input or work field |
l |
l |
Numeric literal |
|
|
l |
l |
Numeric input or work field |
|
|
l |
|
NUMERIC (with input field only) |
|
Alphanumeric or hexadecimal literal |
l |
l |
Alphanumeric or hexadecimal literal |
|
|
l |
l |
Alphanumeric or hexadecimal input or work field |
|
Alphanumeric input or work field |
l |
l |
Alphanumeric or hexadecimal literal |
|
|
l |
l |
Alphanumeric or hexadecimal input or work field |
|
LEVL |
l |
l |
Numeric literal |
|
EOF |
l |
|
None |
Note:
* EQ equal to GT greater than GE greater than or equal to NE not equal to LT less than LE less than or equal to
Indicates the type of test to be performed:
|
Symbol |
Synonym |
What it means |
|---|---|---|
|
EQ |
E or= |
Indicates the values of the left and right operands are equal. |
|
NE |
N or # |
Indicates the values of the left and right operands are not equal. |
|
GT |
H or > |
Indicates the value of the left operand is greater than the value of the right operand. |
|
LT |
L or < |
Indicates the value of the left operand is less than the value of the right operand. |
|
GE |
>= or => |
Indicates the value of the left operand is greater than or equal to the value of the right operand. |
|
LE |
<= or =< |
Indicates the value of the left operand is less than or equal to the value of the right operand. |
The test must be compatible with the type of data contained in the left and right operands; possible combinations of data types and test operations are presented in the Valid Left and Right Operand Data Types and Associated Test Operations table.
A maximum of 32 test conditions can be defined on a single process parameter. One or more test conditions can be enclosed in parentheses. CA Culprit evaluates expressions within parentheses before evaluating expressions not enclosed in parentheses.
A keyword value for the right operand. NUMERIC indicates that the value of the left operand is to be tested for numeric data. Valid test operations with this keyword are EQ and NE. An EQ test is true if the value of the left operand is numeric; a NE test is true if the value of the left operand is not numeric. If nonnumeric data is discovered, the record that contains the nonnumeric data can be dropped from further processing to avoid a data exception.
Specifies either a single numeric literal or field name or a list of numeric literals or field names for comparison, as follows:
Valid test operators for a list of items are EQ and NE. An EQ test operator implies an OR connector between the listed values; a NE test operator implies an AND connector between the listed values.
Syntax and syntax rules for coding field-name-expression appear in User-Defined Variables.
Identifies a range of values in the right operand to be compared to the left operand. The range of values must be enclosed in parentheses; the keyword TO must join the first and last values of the range.
Valid test operators for this expression are EQ and NE. An EQ test operation is true if the value of the left operand equals some value in the specified range, inclusive. A NE test operation is true if the value of the left operand is not equal to any value in the specified range, inclusive.
See expanded syntax diagram above for details of field-name-range.
Logically connects two test operations, as follows:
Expansion of Result-action
In this discussion, the words buffer and control break are used as follows:
Indicates that processing for the current buffer or control break is complete for the report associated with this parameter. Any remaining procedure logic defined for this report is not executed; the code is not accessed again until the next buffer or control break is processed. Once a DROP executes, no additional edit lines are extracted or printed for the current buffer or control break for this report. Information that was output before the DROP instruction is not affected.
Indicates that processing for the current buffer or control break is complete for the report associated with this parameter. Edit lines selected for the buffer or for the control break are extracted or output. Any remaining procedure code defined for the report is not executed for the current buffer or control break.
Indicates that edit lines selected for the current buffer or for the current control break are extracted for output. The remaining procedure code defined for the report is processed. Processing control returns to the procedure statement that immediately follows the RELS instruction.
Any number of RELS statements can be issued for each buffer or control break by each report. The RELS instruction allows information to be extracted or printed for a buffer or control break and allows the buffer or control break to be processed further.
Indicates that processing for the current buffer is complete for the report associated with this parameter; a STOP-RUN instruction in type 7 logic forces an end-of-file condition. All reports in the run finish processing the current buffer. If an EOF test is included anywhere in the run, any logic associated with the test is then executed.
STOP-RUN can appear only on a type 7 process parameter; it must not be coded as the result action of an EOF test. Since all reports processed by a CA Culprit run are affected by a STOP-RUN statement, a warning message is printed in the Input Parameter Listing.
STOP may be used as a synonym for STOP-RUN.
Indicates that processing for the current buffer is complete for the report associated with this parameter and that no further input records are to be processed for this report. Type 7 logic for this report is entered again only when an end-of-file condition is reached and only if an EOF procedure statement is coded for the report. Type 7 logic for other reports in the run continues to execute.
STOP-RPT can appear only on type 7 process parameters; it must not be the result action of an EOF procedure statement.
Causes a special extracted-items record to be written to the extracted items and statistics file; the record contains the current values for all variables, other than sort keys, that are referenced on type 4 edit parameters. HEAD can appear only on a type 7 process parameter.
Values for variable header fields that are not sort keys must be extracted by specifying HEAD as a result action. A HEAD instruction generates additional procedure code and causes special records to be written to the extracted items file. Therefore, it is more efficient to include all variable fields in type 4 edit parameters as sort keys.
Records extracted by a HEAD instruction are sorted in accordance with the values of the related sort-key fields, but ahead of detail lines with the same sort-key values. Header variables extracted by a HEAD instruction are inserted into appropriate header lines in the output phase.
Indicates that processing control is passed to a user-coded or CA-supplied procedure module. Nn is a 2-digit number in the range 00 through 99. USnn can be specified only on a type 7 process parameter that contains a B (branch) or CALL instruction; the B instruction is discussed earlier; the CALL instruction is discussed under Control Operations.
After the named procedure completes execution, processing control returns to the procedure statement immediately following the statement that contains USnn.
Note: For more information on CA Culprit procedure modules, see the CA Culprit for CA IDMS User Modules Guide.
The following figure illustrates how DROP, TAKE, and RELS instructions differ in procedure logic. This figure applies only to type 7 procedure logic; in type 8 procedure logic, the instructions would be processed at the end of the output phase and at each control break.
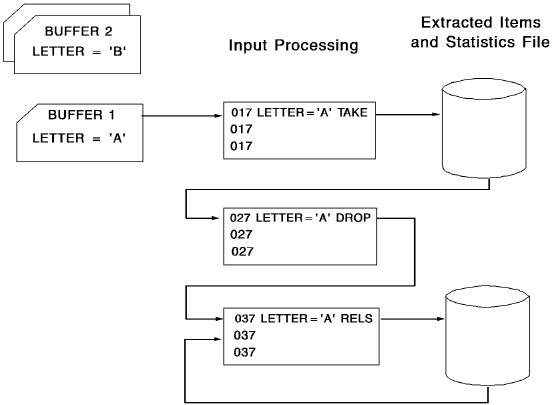
Note: This figure illustrates CA Culprit processing for one input buffer in type 7 procedure logic.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|