

Identifying Source Records in Different Orders to Change Results
The following diagram illustrates the records being used to derive a view:
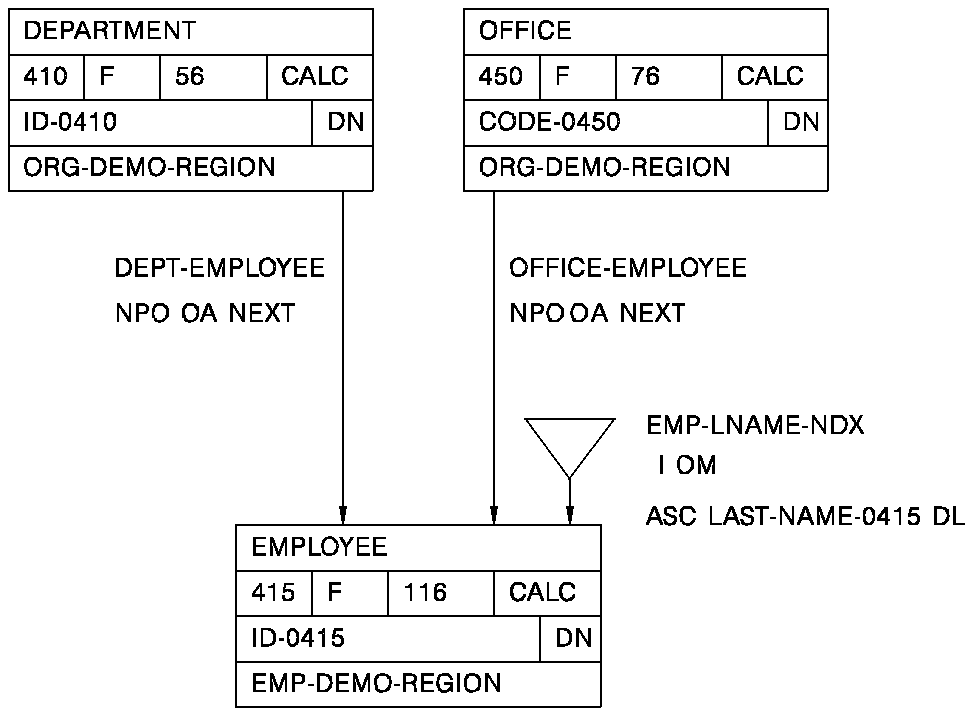
The records are identified in the following order:
Source Record Derivation Source #
DEPARTMENT 01
EMPLOYEE 02
OFFICE 03
The records are joined on the following set relationships:
Column #1/Set Of Der Oper Column #2 Of Der
DEPT-EMPLOYEE 01 ST 02
OFFICE-EMPLOYEE 03 ST 02
The records are obtained as follows:
OBTAIN EACH DEPARTMENT WITHIN area-name OBTAIN EACH EMPLOYEE WITHIN DEPT-EMPLOYEE OBTAIN OWNER WITHIN OFFICE-EMPLOYEE
In this example, any employee not connected to a department will not be returned.
The records are identified in the following order:
Source Record Derivation Source #
EMPLOYEE 01
OFFICE 02
DEPARTMENT 03
The records are joined on the following set relationships:
Column #1/Set Of Der Oper Column #2 Of Der
OFFICE-EMPLOYEE 02 ST 01
DEPT-EMPLOYEE 03 ST 01
The records are obtained as follows:
OBTAIN EACH EMPLOYEE WITHIN area-name OBTAIN OWNER WITHIN OFFICE-EMPLOYEE OBTAIN OWNER WITHIN DEPT-EMPLOYEE
In this example, all employees are returned, though not every employee may be connected to a department or an office.
Defining an Ambiguous Path
The previous diagram illustrates the records being used for derivation.
The records are identified in the following order:
Source Record Derivation Source #
DEPARTMENT 01
OFFICE 02
EMPLOYEE 03
The records are joined on the following set relationships:
Column #1/Set Of Der Oper Column #2 Of Der
DEPT-EMPLOYEE 01 ST 03
OFFICE-EMPLOYEE 02 ST 03
ASF would attempt to build a retrieval path as follows:
OBTAIN EACH DEPARTMENT WITHIN area-name OBTAIN EACH OFFICE WITHIN area-name OBTAIN EACH EMPLOYEE WITHIN DEPT-EMPLOYEE
The OFFICE-EMPLOYEE set join would cause an error because ASF is unable to connect the OFFICE record, which was already obtained, to the EMPLOYEE record obtained through the DEPT-EMPLOYEE set. Since the DEPARTMENT and OFFICE records are not connected through any set relationship, a logical path cannot be built.
Joining Records that Are Already Directly Connected
The following diagram illustrates the records being used for derivation:
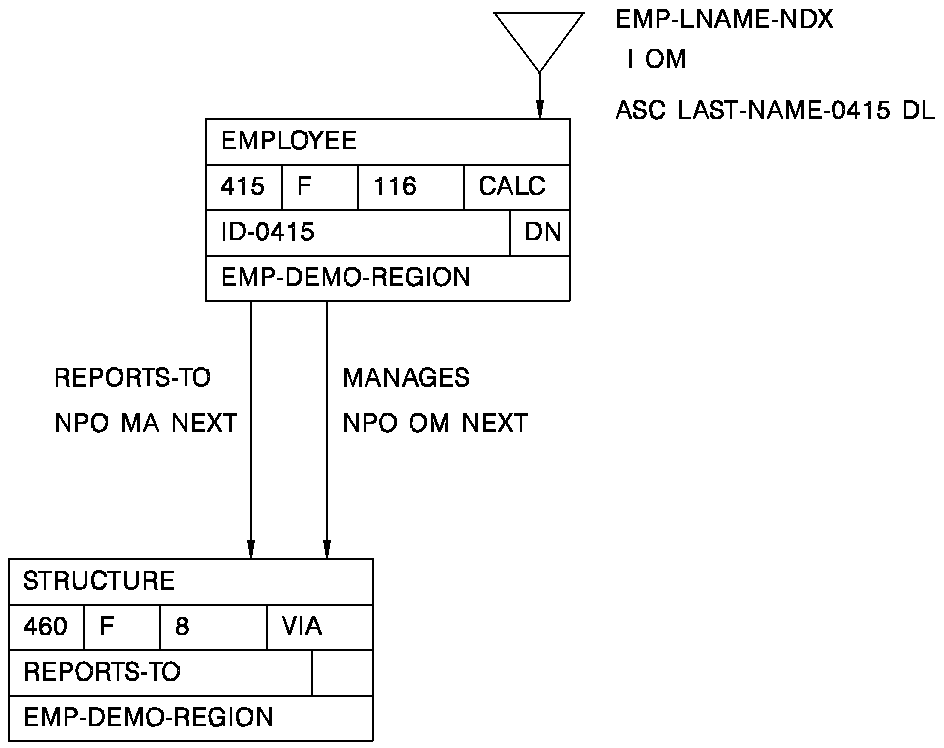
The records are identified as follows:
Source Record Derivation Source #
EMPLOYEE 01
STRUCTURE 02
The join information is entered as follows:
Column #1/Set Of Der Oper Column #2 Of Der
REPORTS-TO 01 ST 02
MANAGES 01 ST 02
The MANAGES set join would not be allowed because the EMPLOYEE and STRUCTURE records are already directly connected through the first join defined.
Note: To include the MANAGES set in the table, identify the EMPLOYEE record again as a separate derivation source (derivation source #3) and specify the following join information:
Column #1/Set Of Der Oper Column #2 Of Der REPORTS-TO 01 ST 02 MANAGES 03 ST 02
Note that the resulting view returns two records of the same record type. Only the last record obtained will be updated in the database when updates are made through the view.
Joining Records that Are Already Indirectly Connected
The following diagram illustrates the records being used for derivation:
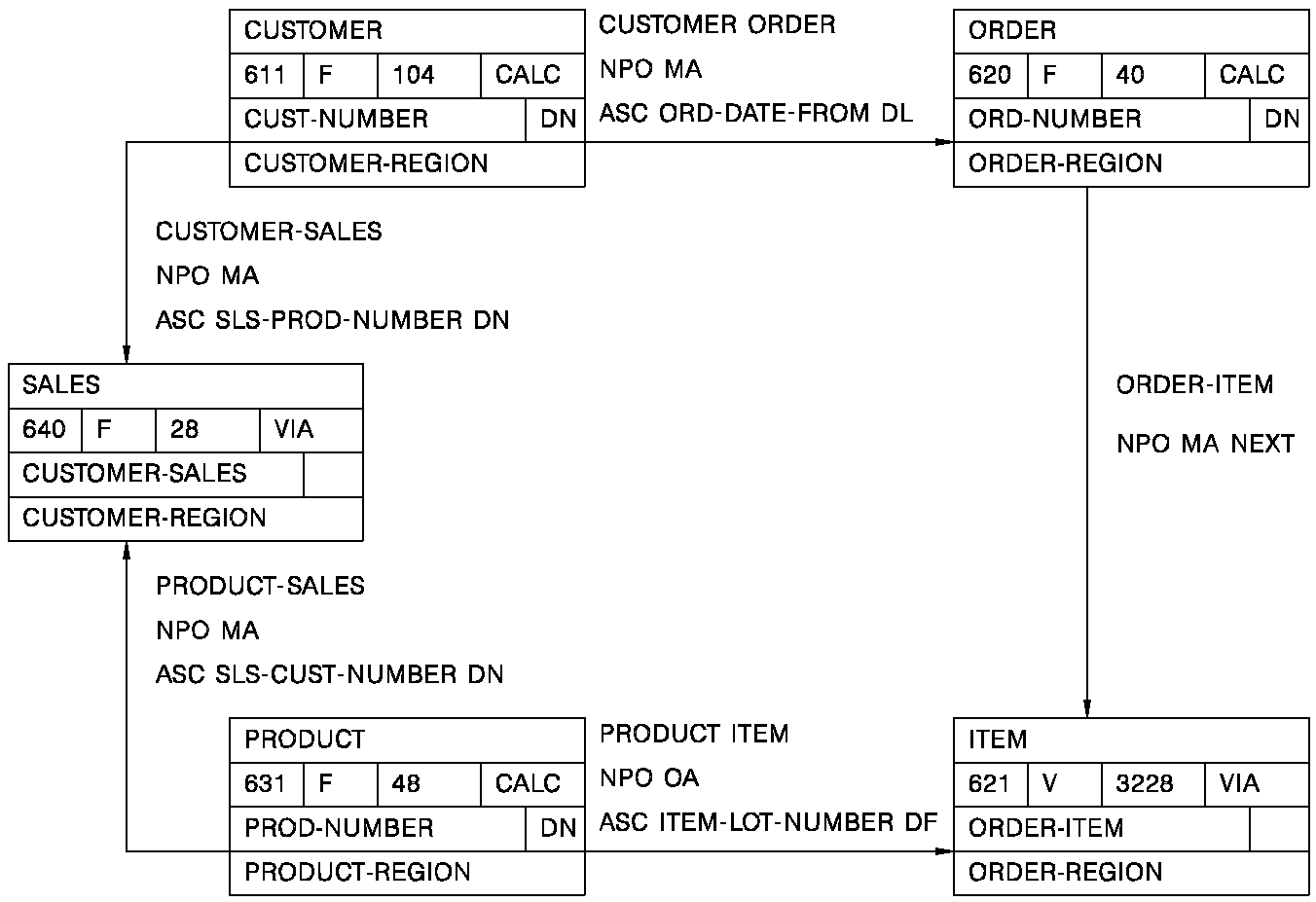
The records are identified as follows:
Source Record Derivation Source #
CUSTOMER 01
SALES 02
PRODUCT 03
ITEM 04
ORDER 05
The join information is entered as follows:
Column #1/Set Of Der Oper Column #2 Of Der
CUSTOMER-SALES 01 ST 02
PRODUCT-SALES 03 ST 02
PRODUCT-ITEM 03 ST 04
ORDER-ITEM 05 ST 04
CUSTOMER-ORDER 01 ST 05
The CUSTOMER-ORDER set join would not be allowed because the CUSTOMER and ORDER records are already indirectly joined through the previously defined set relationships.
When you derive a view from non-SQL defined records, the elements of the schema records become the columns for the view. The following considerations apply:
02 REGION
OCCURS 3.
04 REGIONAL-MANAGER PIC X(20).
04 SALES-MANAGER PIC X(20)
OCCURS 2.
The above element would result in the following columns:
REGION.1 REGIONAL-MANAGER.1 SALES-MANAGER.1.1 SALES-MANAGER.1.2 REGION.2 REGIONAL-MANAGER.2 SALES-MANAGER.2.1 SALES-MANAGER.2.2 REGION.3 REGIONAL-MANAGER.3 SALES-MANAGER.3.1 SALES-MANAGER.3.2
Note: Varying OCCURS clauses (for example, OCCURS DEPENDING ON) are not supported by ASF.
Multiple levels of OCCURS clauses, such as the SALES-MANAGER columns above, are supported by ASF. Online mapping, which creates the screen format for the ASF-generated application, supports first-level OCCURS clauses only. The SALES-MANAGER columns are part of the table definition, but cannot be displayed online through the ASF-generated application.
Note: Views derived from non-SQL defined records cannot be used as source tables for other views.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|