

ADSA screens prompt for information that defines the application structure and runtime flow of control. When the definition is completed and compiled, CA ADS stores the resulting load module in the data dictionary for use at runtime.
Functions
Runtime flow of control is based on the analysis of the interactions (functions) necessary to conduct the work of the application. In a CA ADS application, a function can be any one of the function types listed in the table below. Functions are the structural units of an application. They are defined by using ADSA screens.
Typically, an online application contains menu functions, menu/dialog functions, dialog functions, and many of the system functions. Program functions are less often used.
Functions in a CA ADS application
|
Function Type |
What it Does |
|---|---|
|
Dialog |
Performs a variety of processing activities, such as data retrieval and update |
|
Program |
Performs processing specified in user-written COBOL, PL/I, or Assembler programs |
|
Menu |
Displays a system-defined menu screen Performs standard menu processing activities at runtime |
|
Menu/dialog |
Displays either a system-defined or a site-defined menu screen Performs standard processing and any additional site-defined processing supplied by an associated dialog |
|
System Functions |
Perform predefined activities |
|
ESCAPE |
Bypasses a function even though the current screen contains errors |
|
FORWARD/BACKWARD |
Pages forward or backward on menu maps |
|
HELP |
Displays the runtime Application Help screen |
|
POP |
Returns to the last menu or menu/dialog function |
|
POPTOP |
Returns to the first menu or the menu/dialog function |
|
QUIT |
Terminates application processing |
|
RETURN |
Returns to the next higher level function in the sequence of operative functions |
|
SIGNON/SIGNOFF |
Signs on to or off of CA IDMS/DC or DC/UCF from within the application |
|
TOP |
Returns to the highest level function in the sequence of operative functions |
Responses
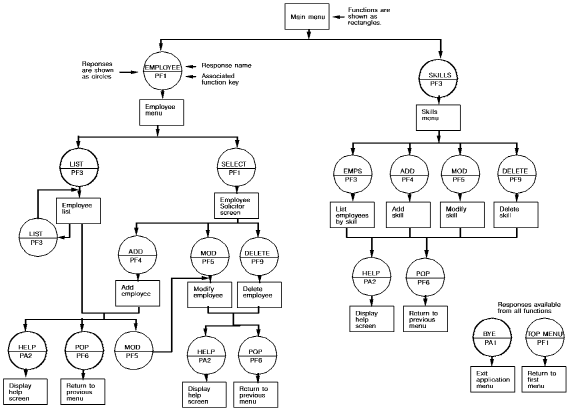
The path between two functions is called a response. Responses define all possible flow of control in the application. The following diagram shows the functions and responses of a sample employee information application that stores and displays employee information.
Functions and responses in a sample CA ADS application
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|