

The following illustration shows the flow in check in and check out processing:
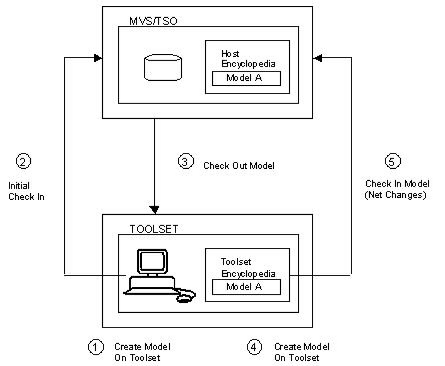
Note: The Host Encyclopedia records the user ID of the person who checks out the model. It does not record the workstation to which the model is checked out.
Because this update is not the initial check in (Step 2), only the changes made to the model are sent to the Host Encyclopedia.
If the model is updated with check in, the model is checked into the Host Encyclopedia, and the Toolset again contains a read‑only version of the model.
Note: If you skip the check out in Step 3, Step 5 fails because the model is not checked out to the user trying to do the check in. Only the user, model owner, or encyclopedia administrator who checked a model out can check the model back in.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|