

It is easy to identify foreign keys and their targets:
All other columns represent properties of the objects in the tables. Details of when to join specific columns are given throughout this chapter.
A typical JOIN, in this case to retrieve all attributes of an entity type, looks like this:
ATTRIBUTE.PARENT_ENTITY_ID = ENTITY_TYPE.ID
The JOIN format, therefore, is:
FROM Table.Foreign Key = TO Table.Target
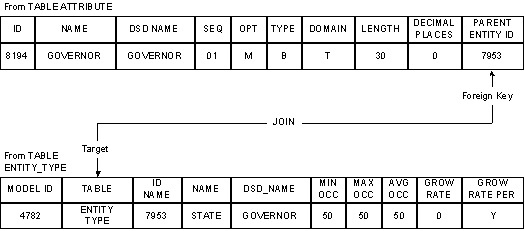
Frequently, the name of the foreign key without the suffix (_ID) is the same as the name of the TO table. In this example, the attribute table can be joined with the entity type table, entity subtype table, or system entity type table (work attribute set) because the PARENT_ENTITY_ID represents the foreign key of one of these three tables.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|