

Two concepts underlie the representation of relationships between entity types: cardinality and optionality. For data models:
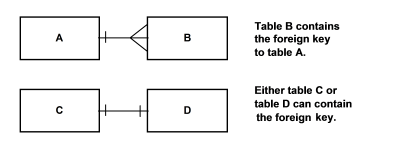
Each relationship in the data models represents an SQL join. Relationships in the data models show both cardinality and optionality. When a relationship has a one-to-many cardinality, the foreign key is on the many side. In a one-to-one relationship, the foreign key can be on either side. The following graphic is a pictorial depiction.
The optionality symbol (a circle on the relationship line) shows whether a table can be empty for a particular occurrence and therefore return no data in an SQL query. The following graphic is a pictorial depiction.
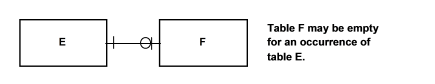
When a relationship is optional on one side, the foreign key is on the optional side. In the example, F contains the foreign key.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|