

Control is passed and results received through event handlers, commands, exit states, flows, remote uses, and so on.
The following illustration provides an example of a task definition.
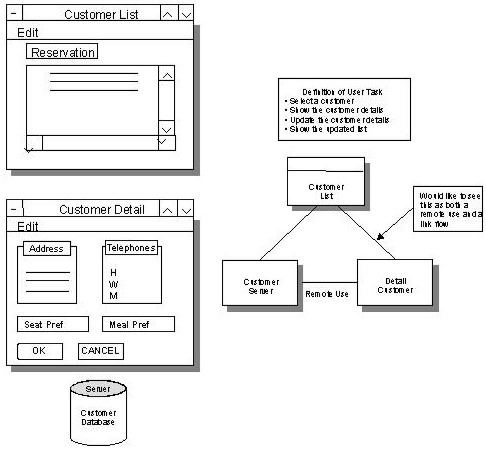
In this example, a design decision was made to use a separate client procedure and its primary window to present the customer detail. The alternative was to have an additional dialog box in the list customer client procedure. This decision was made to keep the amount of information about each customer returning from the customer server to the list customer window to a minimum since it is not necessary. Only when a new customer is added, an exiting customer is updated, or all data about a single customer need to be displayed will the detailed window be used. This choice significantly changes the logic.
It is very helpful if an organization decides on standards for common tasks such as this example. Standards ensure ease of maintenance during and after the development cycle by ensuring consistency of approach. There are user interface standards.
The following illustration and its key provide an example of the control structure. This example illustrates point by point, how control is passed and results are received through event handlers, commands, exit states, flows, and remote uses.
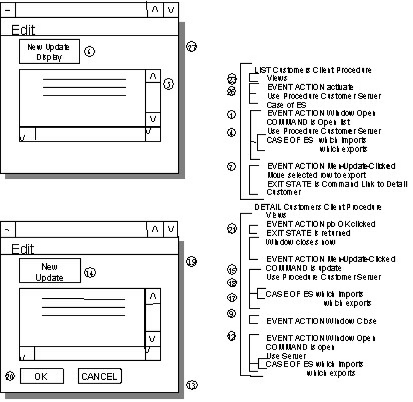
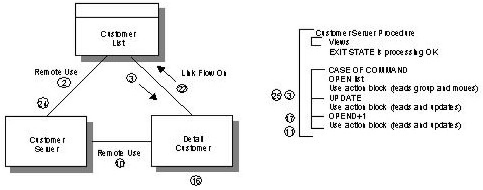
The steps in the next table lead you through the design shown in the illustration. Specific names of objects on the figure are shown in italics in the table.
|
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
|
1 |
The starting state for this example is that there has been a Display First flow to the List Customer window. Note: You can design this into the event handler such that each time the event is executed the command will be set. That is why you do not see any logic to set the command in the event handler. |
|
2 |
Control is passed from the customer list client procedure to the customer server procedure via the window and server managers. |
|
3 |
The customer server procedure processes the request of the customer list client procedure by executing the case of command. Note: The detail of the logic of the action block is not included, nor is the view matching from the server procedure. If there were any problems while trying to read the list of customers, an exit state would have been set. |
|
4 |
Since a remote use statement was used for the procedure interaction, and there is logic after the remote use statement, the control passes back to the OPEN event via the window manager. |
|
5 |
The user is presented with the window containing a list of customers. |
|
6 |
The user clicks on either the edit or update menu items or the update from the tool bar. |
|
7 |
The menu update clicked event moves the selected row to the export view and sets the exit state to link to detail customer. |
|
8 |
Control is passed to the detail customer client procedure. |
|
9 |
The open window event sets the command to opendtl and executes the remote use of the customer server procedure. Note: The command opendtl was included at design time. There is no need for logic to set the command. |
|
10 |
Control is passed from the customer detail client procedure to the customer server procedure via the window and server managers. |
|
11 |
The customer server procedure processes the request of the customer detail client procedure by executing the case of command. Note: The logic detail of the action block is not included, nor is the view matching from the server procedure. If there were any problems while trying to read the list of customers, an exit state would have been set. |
|
12 |
Since a remote use statement was used for the procedure interaction, and there is logic after the remote use statement, control passes back to the OPEN event via the window manager. |
|
13 |
The user is presented with the window containing the detail of the customer previously selected from the list customers. |
|
14 |
The user clicks on either the edit or update menu items or the update from the toolbar. |
|
15 |
The menu update clicked event automatically moves the import view to the export view (you do not have to put this logic in the event handler) and sets the command to update. |
|
16 |
Control is passed to the customer server procedure. |
|
17 |
The customer server procedure processes the request of the customer detail client procedure by executing the case of command. Note: The detail of the logic of the action block is not included, nor is the view matching from the server procedure. If there were any problems while trying to read the list of customers, an exit state would have been set. |
|
18 |
Since a remote use statement was used for the procedure interaction, and there is logic after the remote use statement, the control passes back to the menu update clicked event via the window manager. Note: For this example, there were no errors. The case of exit state logic in the OPEN event is then executed. |
|
19 |
The user is presented with the window containing the detail of the customer previously updated. |
|
20 |
The user clicks the OK push button. |
|
21 |
The pb OK clicked event automatically moves the import view to the export view (you do not have to put this logic in the event handler). |
|
22 |
Control is passed to the list customer client procedure. This client procedure is Display First, flowed to on the return exit state, and contains a view match of the selected customer. |
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|