

A check box is a control that acts like a switch (on/off, yes/no, true/false, and so on) for selecting choices. It consists of a box that displays an X when the user selects it. (In some windows environments, the check box is marked with a _ instead of an X).
Each check box is independent of all other check boxes.
Using check boxes saves space on windows and dialog boxes.
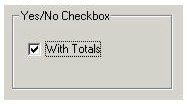
For a yes/no example, you will have a single check box that is labeled With Totals. If the box is marked (selected by the user), the value is yes. If the box is blank, the value is no. The following illustration shows a check box that is marked for true.
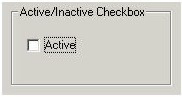
Another example is a check box for an active or inactive customer. The check box is labeled Active. If the box is marked (selected by the user), the customer is active. If the box is blank, the customer is inactive, as is the case in the following illustration.
A check box is associated with an attribute. The true (yes) and false (no) value for the box can be any valid value for the attribute's domain and size selected from its permitted values.
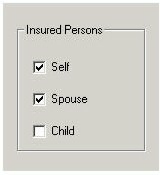
You can group check boxes if you want multiple options to be set on or off. For example, the persons covered by a policy can be selected by a series of check boxes, as shown in the following illustration.
The following list explains guidelines for check boxes:
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|