Federation Manager Guide › Federation Manager Installation › Federation Manager Deployment in a Network › Federation Manager Deployment with SiteMinder › Standalone Mode with the SiteMinder Connector at the Relying Party
Standalone Mode with the SiteMinder Connector at the Relying Party
If Federation Manager is communicating with an existing SiteMinder environment in standalone mode, Federation Manager handles only federated requests.
To work with SiteMinder, Federation Manager has to establish a SiteMinder session with the Policy Server so that when the user requests SiteMinder-protected resources, he is not rechallenged. The federated request is eventually redirected to the target web server, which is protected by a SiteMinder Web Agent.
Note: Federation Manager and the SiteMinder Web Agent need to share the same cookie domain in standalone mode.
The following figure shows a standalone mode architecture using the SiteMinder Connector. This figure is from the perspective of the relying party.
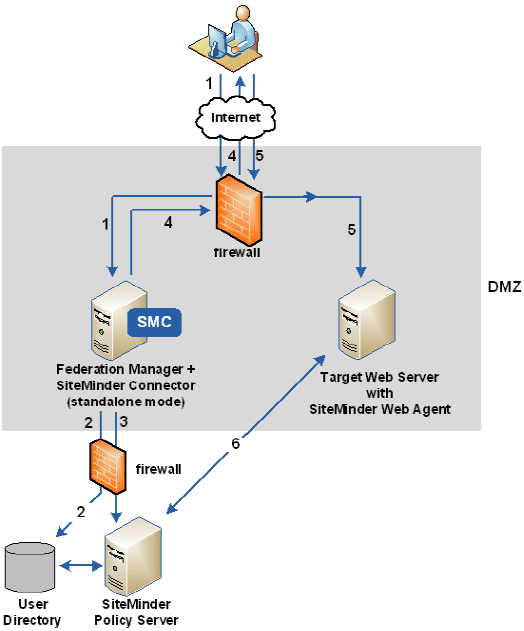
The previous figure shows the following communication flow at the relying party:
- A user requests a federated resource and is redirected to the relying party's assertion consumer service.
- Based on data in the assertion, Federation Manager authenticates the user, which includes communicating with the user directory to complete the user disambiguation process.
- The SiteMinder Connector, as part of Federation Manager, contacts the custom authentication scheme at the SiteMinder Policy Server. A SiteMinder session ticket is created by the Policy Server, which it sends to Federation Manager. Federation Manager then creates a session cookie that includes the ticket. Establishing a SiteMinder session ensures the user is not challenged later when accessing the target resource.
- Federation Manager returns a redirect response back to the user's browser.
- The browser redirects the user to the web server with the target resource, which is protected by the SiteMinder Web Agent.
- The SiteMinder Web Agent and Policy Server complete the authorization process.
After successful authorization, the target resource is presented to the user's browser.
