Federation Manager Agent for Windows Authentication Guide › Introduction to the CA Federation Manager Agent for Windows Authentication › NTLM Protocol
NTLM Protocol
NTLM includes various authentication and session security protocols. NTML is based on a challenge-response model, consisting of three types of messages exchanged in the following order:
- The client sends a type 1 message (negotiation) to the server. The type 1 message specifies the features supported by the client and requested of the server.
- The server sends a type 2 message (challenge) to the client. The primary function of this message is to challenge the identity of the client user.
- The client sends a type 3 message (authentication) to the server. The type 3 message includes the domain and user name of the client user and responds to the challenge in the type 2 message.
The following diagram shows how Federation Manager and the Federation Manager Windows Agent use the NTLM protocol:
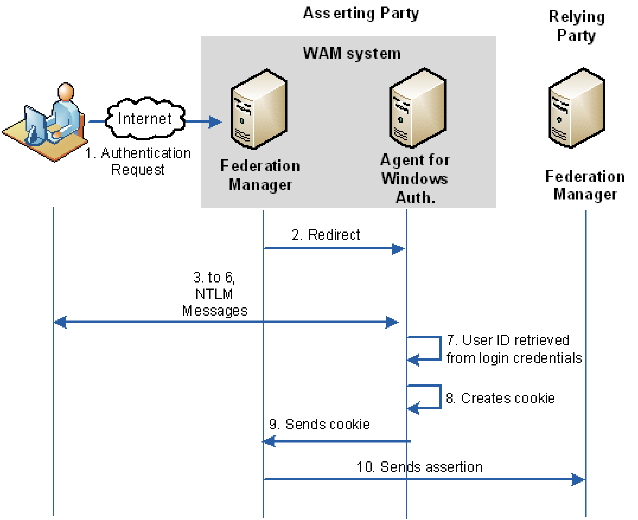
The following process references annotations in the preceding diagram:
- An authentication request is made to Federation Manager at the asserting party.
- Federation Manager recognizes the request as delegated authentication and redirects to the Federation Manager Windows Agent.
- The Federation Manager Windows Agent sends a response back to the browser.
- If the browser is configured for IWA, the browser sends an NTLM Negotiate token (type 1 message) in the authorization header to the Federation Manager Windows Agent.
- The Federation Manager Windows Agent sends an NTLM Challenge token (type 2 message) to the browser.
- The browser sends an NTLM Authenticate token (type 3 message) to the Federation Manager Windows Agent.
- If a security context is associated with a user, the Federation Manager Windows Agent retrieves the user identity from the established context.
- The Agent creates an open format cookie containing the user identity information.
- The Agent sends the cookie to Federation Manager.
- Federation Manager sends a SAML Assertion to the Relying Party to complete federation processing.
|
Copyright © 2012 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|
