Overview Guide › Key Capabilities › Log Storage
Log Storage
CA Enterprise Log Manager provides managed embedded log storage for recently archived databases. Events collected by agents from event sources go through a storage lifecycle as illustrated by the following diagram.
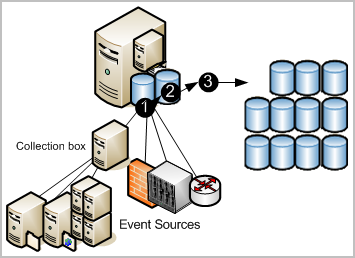
The numbers on the illustration refer to these steps:
- New events collected by any technique are sent to the CA Enterprise Log Manager. The state of incoming events depends on the technique used to collect them. Incoming events must be refined before being inserted into the database.
- When the database of refined records reaches the configured size, all records are compressed into a database and saved with a unique name. Compressing log data reduces the cost of moving it and reduces the cost of storage. The compressed database can either be moved automatically based on auto-archive configuration or you can back it up and move it manually before it reaches the age configured for deletion. (Auto-archived databases are deleted from the source as soon as they are moved.)
- If you configure auto-archive to move the compressed databases to a remote server on a daily basis, you can move these backup to off-site long-term log storage at your convenience. Retaining backups of logs enables you to comply with the regulations that state that logs must be securely collected, centrally stored for a certain number of years, and available for review. (You can restore database from long-term storage at any time.)
Note: See the Implementation Guide for details on configuring the event log store, including how to set up auto-archiving. See the Administration Guide for details on restoring the backups for investigation and reporting.
More information:
Configuring the Event Log Store
Log Storage
Example: Auto-Archiving Across Three Servers
