

The following flowchart reveals the logic flow used when CA Disk processes an SMS managed data set. It should assist you in understanding how the CA Disk SMS sysparms process an SMS managed data set.
The following illustration is an SMS Hierarchy Flow chart:
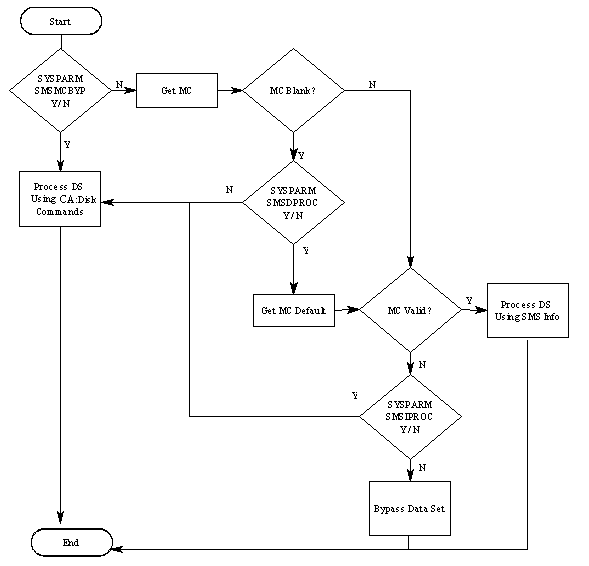
The storage group attributes are used only for the ARCHIVE, BACKUP and VBACKUP functions. The logic flowchart is based on a TRUE and FALSE condition with the TRUE condition being the first exception.
When an SMS managed data set is processed using management class or storage group attributes, the expiration date value in the DSNINDEX record is always set to 99365.
When an SMS managed data set is processed through DSCL bypassing management class or storage group attributes; the expiration date value in the DSNINDEX record is established in 1 of 3 ways:
This is also true for SMS managed data sets with no assigned management class.
When a data set is processed using SMS management class, CA Disk only uses the management class attributes. By default, the expiration date for all SMS managed backup and archive DSNINDEX records is set to 1999.365, but this does not mean they will never expire. Their actual expiration occurs as follows:
For more information about this deletion process, see SMS Information Within The Archives in the chapter "FILES Maintenance." When an SMS data set is processed using CA Disk commands, any management class attributes assigned to the data set are ignored for the execution.
Finally, the IXMAINT & EXPIRE functions honor Management Class attributes as described in the DFSMS Storage Administration Guide. If you are processing GDG data sets, the NOLIMIT values should be fully understood because the action taken depends on the actual definition of the GDG Sphere, especially while you're using the SCRATCH or NOSCRATCH parameters.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|