

Perform the following procedure to activate the VSAM support.
To activate the VSAM support
If you select the first method (supplying the JCL statements directly), see the sysparms VSDEFCAT, VSBIXPSW and VSBIXCAT for consideration. The main drawback to this approach is that it forces all restore and recover jobs that use the same data set names for the work files to be single-threaded (that is, each job must wait until the previous restore has completed and released the exclusive enqueues on the work file data set names). This can cause major processing delays and frustration if there are many restore jobs waiting to be serviced. In addition, the enqueues are left outstanding even if no VSAM data sets need to be restored.
If you select the second method (to leave the IDCUTx dd statements out of the JCL), simultaneous restore jobs can take place (as long as they don't require the same archive tape). When CA Disk restores a VSAM alternate index and determines that BLDINDEX processing needs to be invoked, it checks to see if the IDCUTx dd statements are allocated. If they are not, it generates a unique name for each of the dd statements and allocate them accordingly. Two sysparms govern the allocation of these dd statements.
VSIDCUTPxxxxxxxx—used to specify the high-level node CA Disk is to use for the work file name. For instance, if VSIDCUTPLABS is specified, the generated work file name begins with LABS. If a value is not specified, the high-level node of the first alternate index being built is used. This sysparm is most useful in installations that have not converted to ICF and therefore needs to have the work data set placed on specific volume(s) owned by the VSAM catalog pointed to by the high- level node of the data set name.
Use SIDCUTVxxxxxx...yyyyyy to specify the volume(s) to be used for the work data set. Up to ten volumes can be specified in the list. To use more than one volume, make sure that each of the volumes is specified as exactly six characters (for example, VSIDCUTVWRK800WRK802WRK806). The names that CA Disk generates have the form:
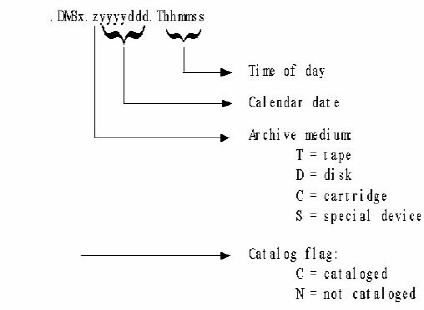
Note: For more information, see the section CA Disk VSAM Date Stamp.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|