

Using CA Service Virtualization › Using the Workstation and Console with CA Service Virtualization › Editing a VSM › JMS VSE Steps
JMS VSE Steps
The following steps are specific to virtual service models that are created using the JMS transport protocol:
- JMS VSE Listen
- JMS VSE Respond
- JMS VSE Live Invocation
During normal operation, the execution flow of the virtual service model is like any other VSE service.
The following graphic uses an overlay to illustrate the flow.
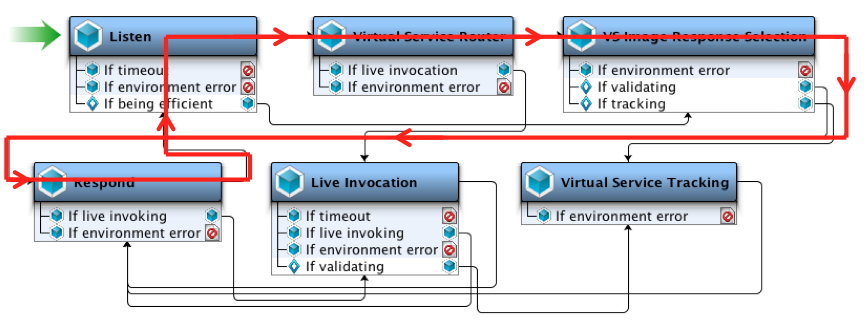
The step with the name Listen is the JMS VSE Listen step. The step with the name Respond is the JMS VSE Respond step. The JMS VSE Live Invocation step is not used.
- The Listen step receives a request message and converts it into a VSE request.
- The Virtual Service Router step routes the flow to the response selection step.
- The VS Image Response Selection step selects a matching transaction from the service image and produces a VSE response.
- The Respond step sends one or more response messages in the VSE response.
- Return to Step 1.
During live invocation, the execution flow of the virtual service model is more complicated.
The following aspects of asynchronous messaging make live invocation difficult:
- A single request can have multiple responses.
- Responses can take any amount of time to be returned.
- In general, it is impossible to determine when all of the responses have been received.
As a result, the Live Invocation step and the Respond step are run in a loop.
The following graphic uses an overlay to illustrate the flow.
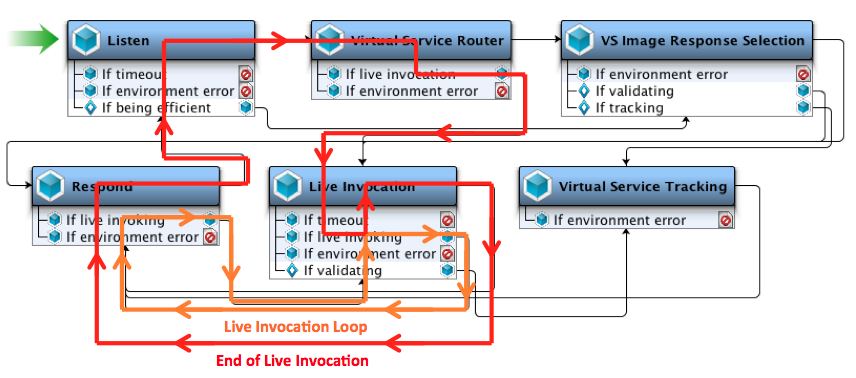
The step with the name Listen is the JMS VSE Listen step. The step with the name Live Invocation is the JMS VSE Live Invocation step. The step with the name Respond is the JMS VSE Respond step.
- The Listen step receives a request message and converts it into a VSE request.
- The Virtual Service Router step routes the flow to the live invocation step.
- The Live Invocation step forwards the request to the live service.
- The Live Invocation step starts listening on every live response queue.
- The Live Invocation step receives a single response from any of the live response queues and converts it into a VSE response.
- The Respond step returns one response message to the client.
- Return to Step 5 and repeat until the Live Invocation step determines that the transaction is complete. Any of the following conditions can cause the Live Invocation step to make this determination:
- The timeout is set and it passes without receiving another response from any of the live response queues. The default value is 30 seconds. The timeout is an advanced parameter that can be set in the VSE recorder or in the Live Invocation step.
- The maximum number of responses is set and that number has been reached. The default value is 1, which indicates that the loop can recur only once. The maximum number of responses is an advanced parameter that can be set in the VSE recorder or in the Live Invocation step.
- The virtual service model is running close enough to capacity that it needs the current model execution thread to break out of its transaction and handle a new request. If the timeout and the maximum number of responses have not been set, this action is the only way for the model to break out of waiting for live responses and loop back to the Listen step.
- The Live Invocation step constructs a final VSE response that contains all of the response messages that went through the loop. The step loops a final time to the Respond step.
- The Respond step does not send any messages on the final loop. Instead, the Respond step completes the typical VSE state cleanup tasks.
- Return to Step 1.
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|



