

The CA Datacom Server JDBC driver is a JDBC 4.0 compliant driver with some exceptions. The JDBC driver implements the JDBC API and requires that your Java programs conform to the JDBC specification. The driver requires a Java virtual machine (JVM) and a JDBC Driver Manager. The Server JDBC driver can operate as a Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, or Type 4 JDBC driver, depending on the type of connection used
The following flowchart shows the JDBC architecture in a UNIX System Services (USS) environment and the relationship of CA Datacom Server to USS applications that use JDBC to access CA Datacom/DB mainframe data from a USS environment.
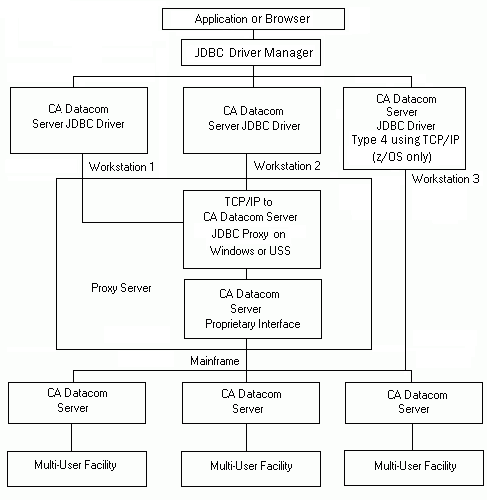
The following information describes each of the JDBC architecture components when used in a USS environment:
Java SQL based applications using the JDBC interface and running under a Java virtual machine (JVM) supporting JDBC 4.0, can access data in a CA Datacom/DB database running as either a 32-bit application or a 64-bit application. An application can be either a stand-alone Java application using JDBC or a web based application that uses some type of web or application server. An application issues a DriverManager.getConnection method or uses the JDBC DataSource interface to connect to the JDBC Driver Manager for a specific driver, such as the Server JDBC driver.
The JDBC Driver Manager is part of the USS Java virtual machine (JVM). Applications connect to the JDBC Driver Manager and the JDBC Driver Manager can connect to any number of drivers. The JDBC Driver Manager forwards an application's connection request to the appropriate driver based on the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) specified in the connection request.
The CA Datacom Server JDBC driver is a JDBC 4.0 compliant driver with some exceptions. The Java classes that constitute the Server JDBC driver reside in the cadcjdbc.jar file.
Drivers that are connected by the JDBC Driver Manager interpret calls from the application and the JDBC Driver Manager, and make calls to the requested DBMS. The Server JDBC DataSource classes can be used to produce Connection objects that participate in connection pooling, and in subsequent release distributed transactions.
The CA Datacom Server provides the use of a Type 4 driver. The Type 4 driver allows direct connection to the server address space using pure Java connections using TCP/IP to the mainframe server. This connection method is invoked by a connection URL as //host:port/ where host is the IP address of DNS name of the host machine where the Mainframe Server component resides, and the port number is the port specified in the Mainframe Server startup parameter TCPIP_PORT=.
The Proprietary Interface (libcadcdb32.so or libcadcdb64.so) provides the CA Datacom/DB interface, data mapping, data translation, and data communication services for Type2 or Type 3 driver connections. It also supplies the CAICCI or native TCP/IP interface (z/OS only). This is the traditional method of connecting a JDBC application to the Mainframe Server component.
A CCI request through a Type 2 or Type 3 driver connection is sent through CAICCI-PC and CAICCI to the Mainframe Server on the host mainframe.
A native TCP/IP request from a Type 4 driver connection (z/OS only) bypasses the Proprietary Interface and is sent directly to the Mainframe Server.
The CA Datacom Server JDBC Proxy is an optional background process that provides a TCP/IP interface (z/OS only) for Type 3 driver connections. The JDBC Proxy can run under a Windows server or under USS (z/OS only). The Proxy is invoked if specified by the connection URL as //host:port/ where host is the IP address of DNS name of the host mainframe where the Proxy resides, and port is the listener port assigned to the Proxy.
CAICCI isolates CA Datacom Server from the communication protocol used between USS and the CA Datacom Mainframe Server component. CAICCI in USS is optional. Through JDBC Data Source Properties or the connection URL, you may choose the type of connection for the application.
CAICCI is required on the host mainframe and is used for communication between Mainframe Server regions and the Server SVCOMPR utility.
In a z/OS environment, the Mainframe Server provides support for native TCP/IP data transmission between workstations and host mainframes. Through startup parameters you can choose to allow native TCP/IP transmissions. If a JDBC Type 4 driver is desired, TCP/IP must be allowed in the Mainframe Server startup parameters.
CA Datacom Server Mainframe Server component executes in its own address space and connects to a specific MUF. It processes connect requests from client applications, handles data transmission requests to and from client applications, and translates data between MUF and client applications.
In a z/OS USS environment, the Mainframe Server component provides support for native TCP/IP data transmission between workstations and host mainframes. Through startup parameters you can choose to allow native TCP/IP transmissions
A MUF provides the ability to access any CA Datacom/DB database concurrently from multiple regions. Each server communicates with only one MUF, but a system can have multiple MUFs accessed by multiple servers or multiple servers accessing the same MUF.
CA Datacom Server JDBC driver is a JDBC 4.0 compliant driver with some exceptions. The JDBC driver implements the JDBC API and requires that your Java programs conform to the JDBC specification. This driver requires a Java virtual machine (JVM) and a JDBC Driver Manager. In a UNIX or Linux environment, the Server JDBC driver can operate as a Type 3, or Type 4 JDBC driver, depending on the type of connection used.
The following flowchart shows the JDBC architecture in a UNIX/Linux environment and the relationship of CA Datacom Server to UNIX/Linux applications that use JDBC to access CA Datacom/DB mainframe data from a UNIX/Linux environment.

The following information describes each of the JDBC architecture components when used in a UNIX or Linux environment:
Java SQL based applications using the JDBC interface and running under a Java virtual machine supporting JDBC 4.0, can access data in a CA Datacom/DB database. An application issues a DriverManager.getConnection or Datasource connection request to the JDBC Driver Manager for a specific driver, such as CA Datacom Server.
The JDBC Driver Manager is part of the USS Java virtual machine (JVM). The applications can connect to the JDBC Driver Manager and the JDBC Driver Manager can connect to any number of drivers. The JDBC Driver Manager forwards an application's connection request to the appropriate driver based on the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) specified in the connection request.
The CA Datacom Server JDBC driver is a JDBC 4.0 compliant driver with some exceptions. The JAVA classes that constitute the Server JDBC driver reside in the cadcjdbc.jar file.
Drivers connected by the JDBC Driver Manager, interpret calls from the application and the JDBC Driver Manager and make calls to the requested DBMS. The Server JDBC DataSource classes can be used to produce Connection objects that participate in connection pooling, and in subsequent release distributed transactions.
The CA Datacom Server provides the use of a Type 4 driver, which allows direct connection to the server address space using pure java connections using TCP/IP to the mainframe server. This connection method is invoked by a connection URL as //host:port/ where host is the IP address of DNS name of the host machine where the Mainframe Server component resides, and the port is the port number specified in the Mainframe Server startup parameter TCPIP_PORT=.
CAICCI isolates CA Datacom Server from the communication protocol used between the Server JDBC Proxy and Mainframe Server component. CAICCI in USS and CAICCI-PC in Windows is optional. Through JDBC Data Source Properties or the connection URL, you can choose the type of connection for the application.
CAICCI is required on the host mainframe and is used for communication between Mainframe Server regions and the Server SVCOMPR utility.
In a z/OS environment, the Mainframe Server provides support for native TCP/IP data transmission between workstations and host mainframes. Through startup parameters, you can allow native TCP/IP transmissions. If a JDBC Type 4 driver is desired, TCP/IP must be allowed in the Mainframe Server startup parameters.
There is no CA Datacom Server Proprietary Interface available for UNIX or Linux. Traditionally, the connection method from a UNIX/Linux based application is through a Type 3 driver which requires a CA Datacom Server Proxy. The Proxy can reside on USS or Windows and the Proprietary Interface resides with it. Another option would be to use a Type 4 driver to connect directly to CA Datacom Server. A Type 4 driver connection only requires that the jar file (cadcjdbc.jar) be included in the application CLASSPATH and the proper connect string be specified. The connect string must include a URL that contains //jdbc:datacom//xxxxxxx:ppppp, where xxxxxxxx is the host name or number and ppppp is the port number specified in the CA Datacom Server mainframe startup parameter TCPIP_PORT=.
The libcadcdb32.so/libcadcdb64.so modules (USS) or the cadcdb32.dll/cadcdb64.dll modules (Windows) provide the CA Datacom/DB Proprietary Interface, data mapping, data translation, and data communication services for Type 3 driver connections. It also supplies the CAICCI or native TCP/IP interface (z/OS only). This is the traditional method of connecting a JDBC application from UNIX or Linux to the Mainframe Server component .
There is no CA Datacom Server JDBC Proxy available for UNIX or Linux. Traditionally, a UNIX or Linux based application connects as a Type 3 driver connection through a JDBC Proxy running on either USS or Windows. In prior releases of CA Datacom Server, this was the only way in which a UNIX or Linux based application could access CA Datacom/DB data.
The CA Datacom Server JDBC Proxy is an optional background process that provides a TCP/IP interface (z/OS only) for Type 3 driver connections. The Proxy can run either a Windows server or under USS (z/OS only). The Proxy is invoked if specified by the connection URL as //host:port/ where host is the IP address of DNS name of the host mainframe where the Proxy resides, and port is the listener port assigned to the Proxy.
The CA Datacom Server Mainframe Server component executes in its own address space and connects to a specific MUF. It processes connect requests from client applications, handles data transmission requests to and from client applications and translates data between MUF and client applications.
In a z/OS environment, the Mainframe Server component provides support for native TCP/IP data transmission between workstations and host mainframes. Through startup parameters, you can allow native TCP/IP transmissions. If a JDBC Type 4 driver is desired, TCP/IP must be allowed in the Mainframe Server startup parameters.
A MUF provides the ability to access any CA Datacom/DB database concurrently from multiple regions. Each server communicates with only one MUF, but a system can have multiple MUFs accessed by multiple servers or multiple servers accessing the same MUF.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|